B
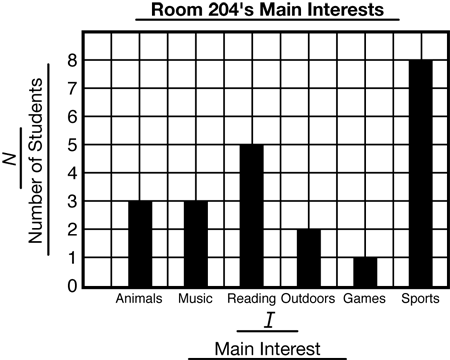
bar graph
A graph that uses bars to show data.
page 4
base
The part of a three-dimensional shape (polyhedron) that sits on the “ground.”
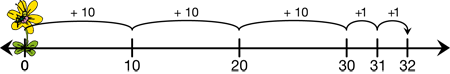
base-ten hoppers
Hoppers that can make hops with distances of one, ten, and one hundred on number lines. They can go forward or backward.
(See also mathhoppers.)
pages 86–90
base-ten pieces
A set of blocks used to model our number system. Note that a skinny is made of 10 bits, a flat is made of 100 bits, and a pack is made of 1000 bits.

pages 71, 73, 79, 129–131, 137, 140–141, 158–160
base-ten recording sheet
A tool to help organize base-ten pieces when they are used to represent numbers. In the example, 283 is represented.
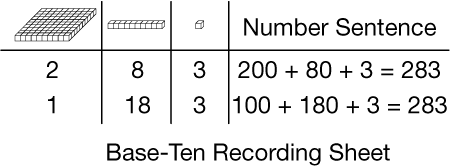
pages 79, 137, 139, 140, 142, 161
base-ten shorthand
A picture drawn to represent the base-ten pieces.
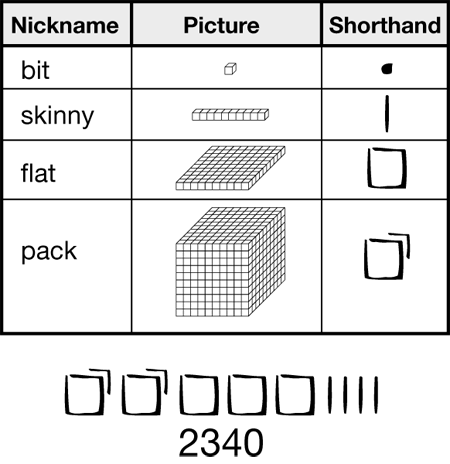
pages 73, 74, 79, 83–85, 131, 158–160
benchmark
Numbers convenient for comparing and ordering numbers (e.g., 0, 50, and 100 are convenient benchmarks for comparing whole numbers).
benchmark numbers
Numbers that are used to compare to when estimating or rounding.
(See also convenient number and friendly numbers.)
best-fit line
The line that comes closest to the most number of points on a point graph.
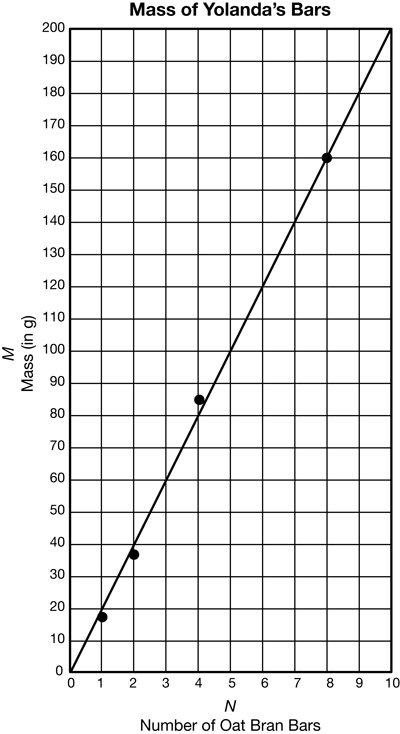
pages 330–347, 355, 358–359
bit
The smallest of the base-ten pieces that is often used to represent 1.
(See also base-ten pieces.)
pages 12, 70, 71, 73, 79, 159
breaking addends
Breaking a number into parts to help make ten with other addends in the problem.
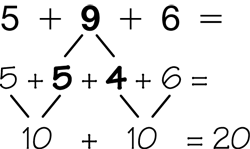
page 19