E
edge
A line segment where two faces of a three-dimensional figure meet.

pages 210, 295, 306, 307–309, 317–318, 319, 321–322
elapsed time
The measurement of how long an event lasts from its beginning to its end.
page 300
equal
The same value. For example, 5¢ is equal to 1 nickel.
pages 16, 19, 43, 62–63, 136, 156, 163, 165–166, 196, 202, 204, 366–367
equal parts
Pieces or parts of a whole that are the same size.
pages 62–63, 202, 207, 250–258, 287–289, 290, 365, 373–376, 377
equal to
Having the same value (=).
pages 165, 247, 251, 254–256, 366
equal-arm balance
A tool for measuring the mass of an object by balancing the object in one pan and a number of standard masses in the other pan.
(See also two-pan balance.)
pages 348–351
equilateral
A shape with all sides and all angles equal.
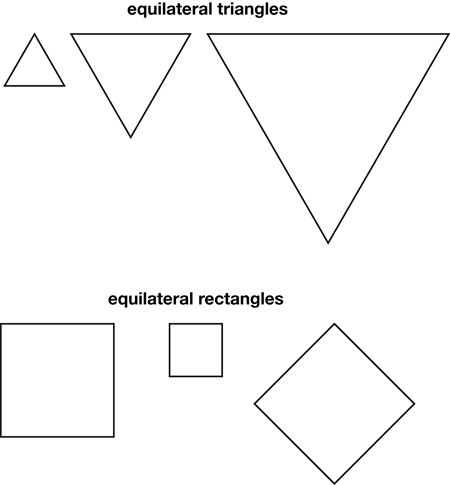
page 294
equivalent
The same as or equal to. For example, 


pages 259–261
equivalent fractions
Fractions that represent the same part of the whole. For example, 


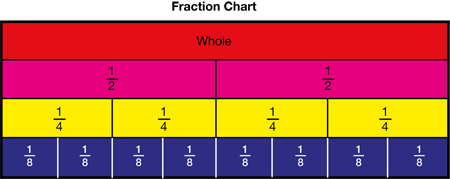
pages 250–251, 259–261
estimate
1. (verb) To find about how many.
2. (noun) An approximate number or a good guess.
pages 100, 122, 133, 135, 144, 184, 186, 243, 329, 351–352, 355, 370, 403–404, 406, 408
exact number
A precise answer. The opposite of an estimate.
pages 122, 135, 186, 329, 360
expanded form
Shows a number expanded into its place value parts. For example, 300 + 40 + 2 is 342 in expanded form. This form can be used to add or subtract.
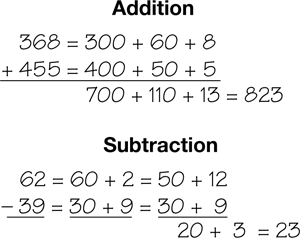
pages 130–131, 144, 156
extrapolation
Using patterns in data to make predictions or to estimate values that lie beyond the range of values in the set of data.
(See also interpolation.)