Students explore the relationship between the circumference and the diameter of circles, record their measurements in a data table, plot them on a graph, and analyze their results. Students find that the circumference of a circle is about three times its diameter and equal to π times the diameter.
Content in this Lesson
- Identifying the parts of a circle [E5].
- Investigating the relationship between circumference and diameter.
- Representing the relationship between variables as a ratio [E2].
- Defining π as the ratio of circumference to diameter of a circle.
- Finding and expressing the relationship between the circumference and the diameter of circles: C = π × D.
- Finding equivalent fractions and ratios using a variety of strategies (e.g., using models, using multiplication and division, using graphs and tables) [E3].
- Using ratios and proportions to solve problems [E4].
- Measuring the circumference of a circle to the nearest tenth of a centimeter [E8].
- Representing the variables and procedures of an investigation in a drawing [E9].
- Collecting and organizing data into a table and line graph to represent the relationship between variables [E10].
- Making point graphs and drawing best-fit lines to represent ratios and proportional relationships [E11].
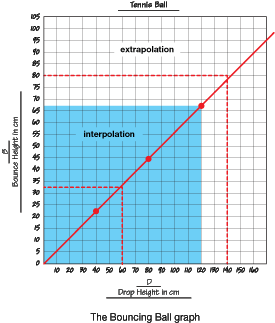
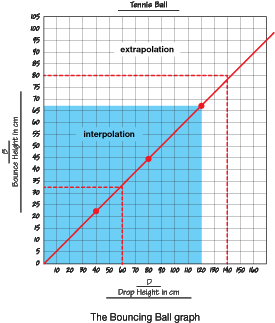
- Using patterns in tables and line graphs to make predictions and solve problems [E12].
- Knowing the problem [MPE1].
- Using labels [MPE6].
Assessment in this Lesson
| Assessment | Expectation Assessed | Math Practices Expectation Assessed |
|---|---|---|
|
Explore Circumference and Diameter Lab |
|
|
|
Explore Circumference and Diameter |
|
|
|
DPP Item X |
|
|
|
DPP Item DD |
|















 = 3.14159265358979323846 . . .
= 3.14159265358979323846 . . .