A
addend
The numbers that are added in an addition problem are the addends. For example, in the problem 8 + 6, 8 and 6 are the addends.
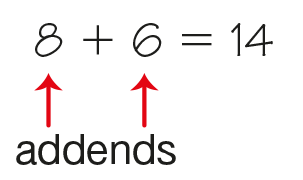
addition
Finding the total of two or more numbers. For example, 45 + 3 = 48. The symbol to show addition is +.
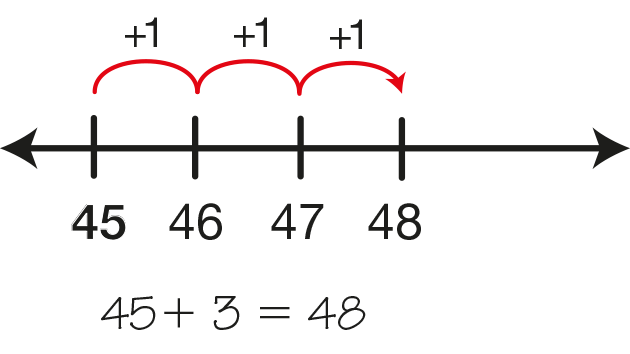
all-partials method
A paper-and-pencil method for solving addition problems. For this method, students add the tens, add the ones, and record partial sums on separate lines. It does not matter whether a student starts with the ones or tens.
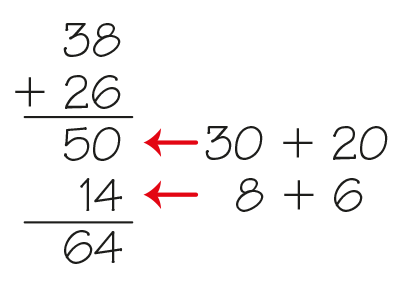
AM
The time period from midnight to noon.
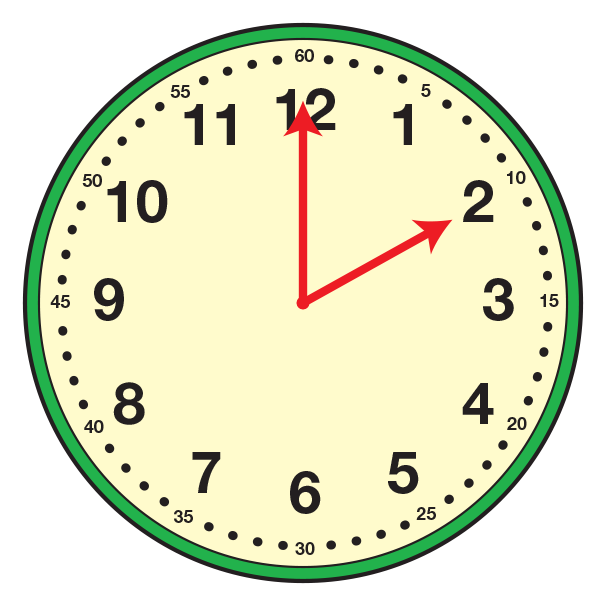
analog clock
A clock with hours marked from 1 to 12. The position of the hour and minute hands show the time.
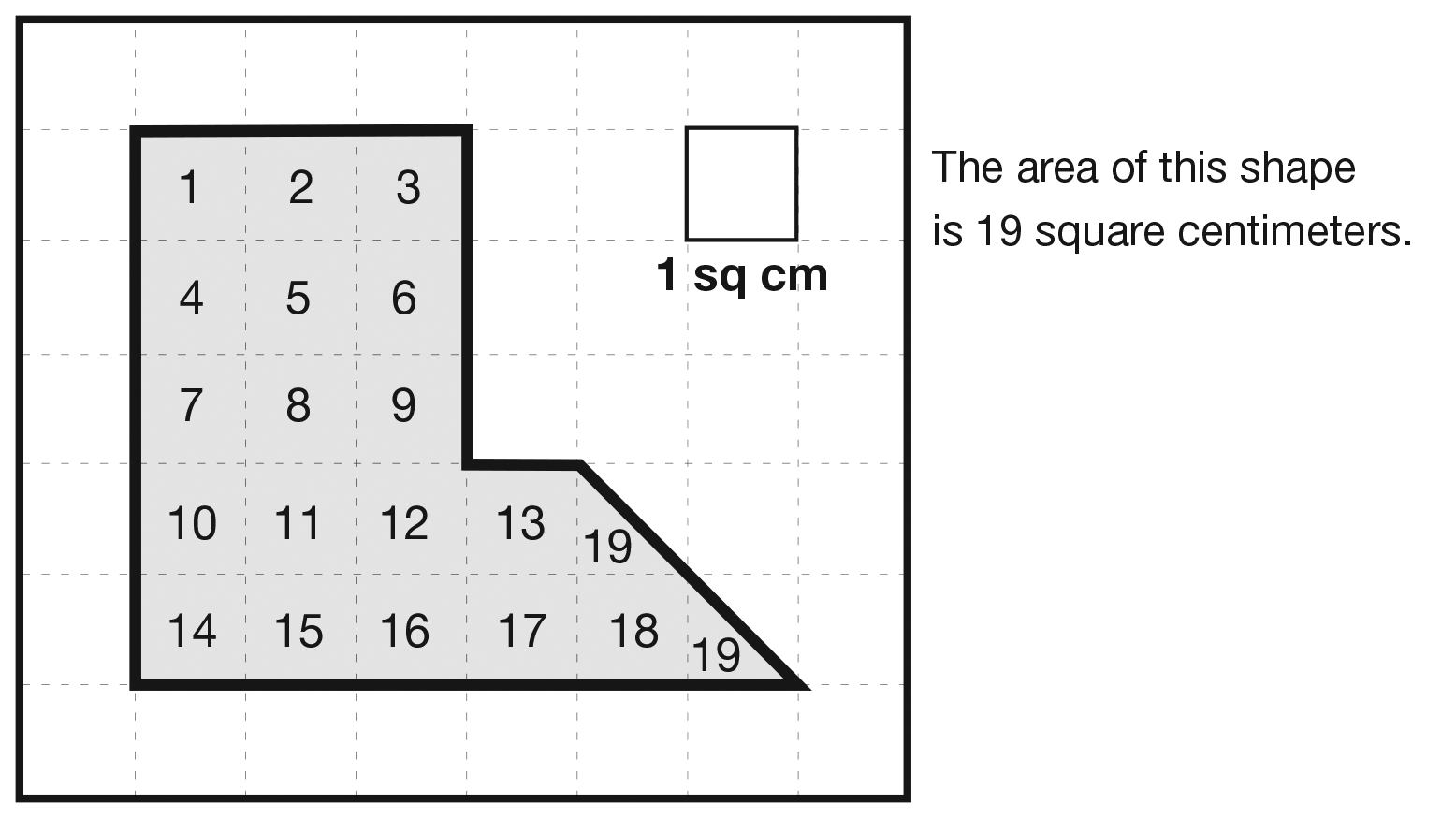
area
The amount of space that a shape covers. Area is measured in square units.
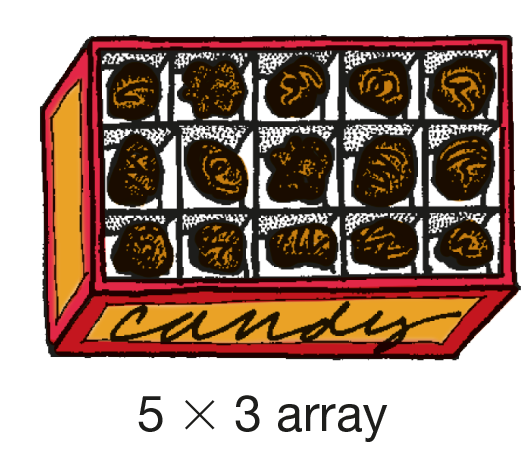
array
An arrangement of objects into a rectangular pattern of rows (horizontal) and columns (vertical). (See also row and column.)

associative property of addition
When you have 3 or more addends, the sum is the same no matter how you group the numbers. For example, (2 + 3) + 4 = 2 + (3 + 4).
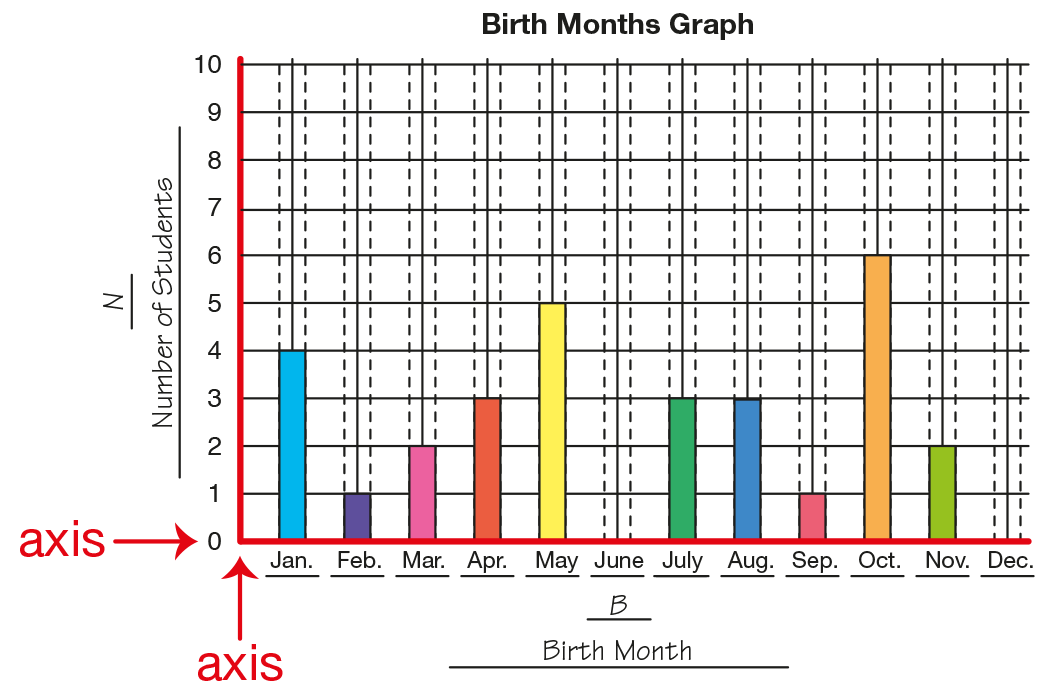
axis
Reference lines on graphs and grids. The horizontal and vertical axes meet at the origin or zero. The plural of axis is axes.