F
fact family
Related math facts, e.g., 3 × 4 = 12, 4 × 3 = 12, 12 ÷ 3 = 4, 12 ÷ 4 = 3.
pages 55–57
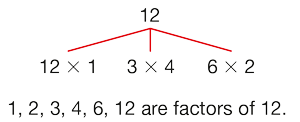
factors
The numbers that are multiplied together to get a new number. In the problem 3 × 4 = 12, 3 and 4 are factors of 12.
pages 54, 65, 96, 112, 137, 407, 422–427, 442–445
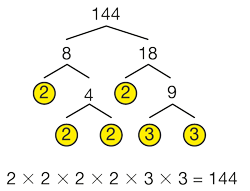
factor tree
A diagram that shows the prime factorization of a number.
pages 443, 445
fixed variable
A variable in an experiment that is held constant or not changed.
pages 231, 351
formula
A number sentence that gives a general rule. A formula for finding the area of a rectangle is Area = length × width, or A = l × w.
pages 331, 434–437, 439–441, 556–557
fraction
A number that is a part of a whole that can be written  where a and b are whole numbers and b is not zero. For example,
where a and b are whole numbers and b is not zero. For example, 




pages 58–63, 64–68, 69–73, 74–75, 76–79, 80–81, 82–85, 86–88, 89–99, 100–104, 105–118, 210–215, 216–220, 238–239, 362–367, 458–459, 460–465, 466–469, 479, 480–497, 498–502, 503–507, 508–514, 515–516, 518–525
function (machine, table)
A rule that assigns to every input number exactly one output number.
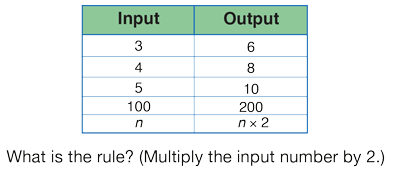
pages 399, 473, 478, 497, 507, 513