B
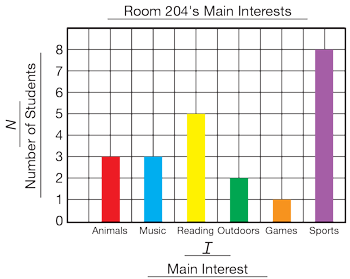
bar graph
A graph that uses bars to show data.
pages 6, 37, 41, 43, 44, 46, 48, 51, 352, 383, 386–387, 520, 554
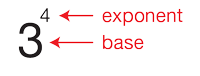
base (of an exponent)
When exponents are used, the number being multiplied is the base. In 34 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 = 81, the 3 is the base and the 4 is the exponent.
(See also exponent.)
page 153
base-ten hopper
A hopper that can make hops with distances of one, ten, one hundred, and one thousand on number lines. Base-ten hoppers can go forward or backward.

pages 129–135
baseline
An initial measurement that is later used for comparison.
benchmarks
Numbers convenient for comparing and ordering numbers, e.g., 0, 
pages 82–84, 105–106, 126–127, 136, 376–377
best-fit line
The line that comes closest to the points on a point graph.
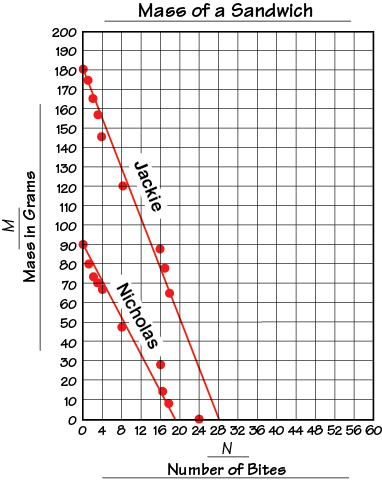
pages 228, 232, 354, 438, 523, 541, 544, 555, 576, 580–581
billion
A number equal to one thousand million (1,000,000,000).
pages 121, 124, 136, 146–147
binning data
Placing data from a data set with a large number of values or large range into intervals in order to more easily see patterns in the data.
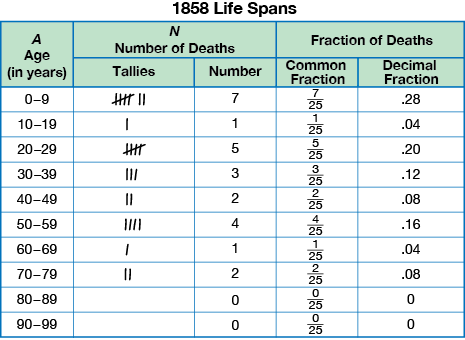
pages 381, 386