S
sample
A part or subset of a population.
pages 36–41, 385, 560–581
sampling
A small group of people or things taken from a larger group or used to represent the larger group.
pages 36–41, 385, 560–581
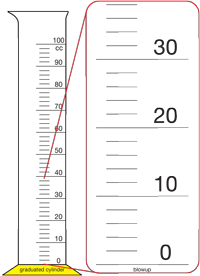
scale
A series of spaces marked by lines, dots, or numbers that is used for measuring quantities.
pages 236–237, 272–273, 274–275
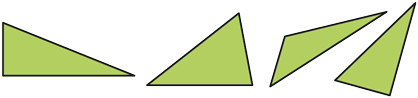
scalene triangle
A triangle whose sides are all different lengths.
side
The edge of a polygon.

pages 186–188, 189–190
sieve
A method for separating prime numbers from nonprime numbers developed by Eratosthenes, an Egyptian librarian, in about 240 bce.
pages 429–431, 449
simplest form
A fraction that has a numerator and denominator that have no factor in common except 1. (See also reducing fractions.)
pages 210–215, 219–220, 238–239
speed
The ratio of distance moved to time taken; e.g., or 3 mph is
or 3 mph is
a speed.
pages 230–235
square
A polygon with four equal sides and four right angles.
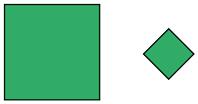
pages 55, 187–188, 189, 281, 288, 290–292, 369–370, 412, 432–437, 438–441
square centimeter
The area of a square with a side length of one centimeter.
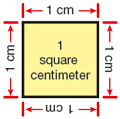
pages 186, 189–194, 335–337
square number
A number that is the result of multiplying a whole number by itself. For example, 36 is a square number since 36 = 6 × 6.
pages 56, 438–441, 531
standard form
Writing a number using one digit for each place value (e.g., 457 is standard form for 400 + 50 + 7, which is expanded form).
pages 123–124
standard units
Internationally or nationally agreed-upon units used in measuring variables; e.g., centimeters and inches are standard units used to measure length and square centimeters and square inches are used to measure area.
pages 329–331, 334
strategy
A method or plan for solving a problem.
pages 64–65, 87–88, 103–104, 106, 111, 137, 161–165
sum
The answer to an addition problem.
pages 86–88, 91, 96, 98, 108–110, 382, 392–393, 404–405, 407, 458–459, 478, 479
survey
An investigation conducted by collecting data from a sample of a population and then analyzing it. Surveys are used to make predictions about the entire population.
pages 2–3, 10, 16, 17–19, 40, 45–46, 214, 362, 367, 559