I
improper fraction
A fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator; e.g., 


pages 70–73, 468–469, 470–473, 475, 477–478, 497, 513
infinite
Never ending, immeasurably great, unlimited.
page 149
interpolate (interpolation)
Making predictions or estimating values that lie between data points in a set of data. (See also extrapolate.)
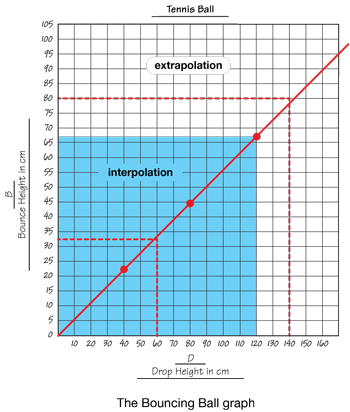
pages 521, 545, 549, 555
inverse operations
Operations that undo each other. For example, addition and subtraction are inverse operations and multiplication and division are inverse operations.
isosceles
Having two equal sides. Often used to describe a triangle with two equal sides and two equal angles.

pages 283–284