A
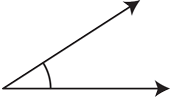
acute angle
An angle that measures less than 90°.
page 291
acute triangle
A triangle whose angles each measure less than 90°.

pages 283–284
all–partials method
A paper-and-pencil method for solving addition and multiplication problems. Each partial product or sum is recorded on a separate line. (See also partial product.)

pages 168–169, 171, 178–180, 200
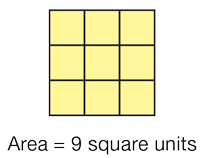
area
The area of a shape is the amount of space it covers, measured in square units.
pages 144, 186–188, 189–194, 329, 331, 333, 335–337, 351–356, 405, 408, 503–504, 529
array model
An arrangement of elements into a rectangular pattern of (horizontal) rows and (vertical) columns.
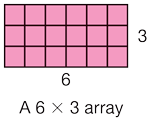
page 307
average
A number that can be used to represent a typical value in a set of data. (See also mean, mode, and median.)
pages 10–16, 19–21, 33, 339–349, 570–571
axes
Reference lines on graphs and grids. The axes are two perpendicular lines that cross at the origin or zero. The singular of axes is axis.
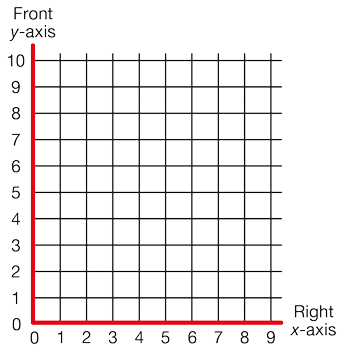
pages 6, 217, 220, 224, 228, 232, 249–254, 255–270, 271–273, 276–277