F
face
The polygons that make up the surface of a three-dimensional shape are called faces. For example, all the faces of a cube are squares.

pages 317–318, 319–320, 321–322
fact family
Related math facts (e.g., 3 × 4 = 12, 4 × 3 = 12, 12 ÷ 3 = 4, 12 ÷ 4 = 3).
pages 45, 208
factors
The numbers that are multiplied together to get a new number. For example, 3 × 4 = 12. The factors of 12 are 3 and 4.
pages 63, 201, 204, 367
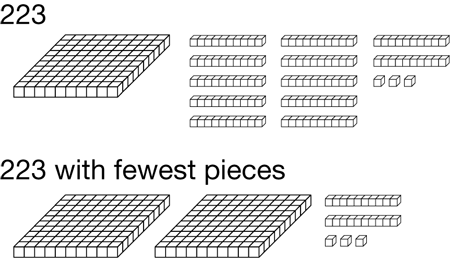
fewest pieces rule
Using the least number of base-ten pieces to represent a number.
(See also base-ten pieces.)
pages 74, 77, 79, 83, 92, 129–130, 138, 140
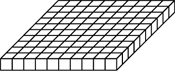
flat
One of the base-ten pieces that is often used to represent 100. The block is a 10 × 10 × 1 arrangement of bits.
(See also base-ten pieces.)
pages 71–76, 78–82, 129, 140–142, 158, 161–165
flat surface
A surface that is not curved.
fraction
A number that is written to show the parts of the whole. The bottom number (the denominator) shows how many parts the whole is divided into and the top number (the numerator) shows how many of those parts you have. For example, 


(See also common fraction and decimal fraction.)
pages 246–248, 249–252, 253–257, 258–261, 262–263, 264–265, 266–280
frequency
The number of times something happens.
pages 3, 6, 13
friendly numbers
Numbers that are easy to calculate to help find a reasonable estimate. In the examples below, friendly numbers are used to estimate a sum or difference.
(See also convenient number and benchmark numbers).
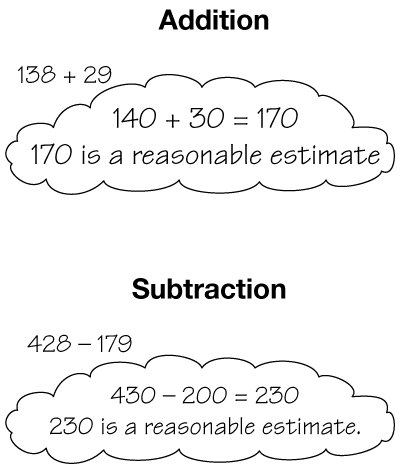
page 354
front-end estimation
Estimation by looking at the left-most digit. For example, to estimate the difference between 567 and 232, the friendly numbers of 500 − 200 are used.
(See also friendly numbers and convenient number.)
front/back axis
The vertical (y) axis on a coordinate grid. (See also left/right axis.)
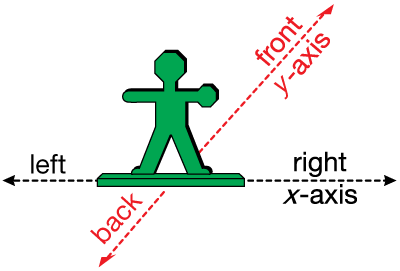
page 324
function (machine, table)
Functions are important mathematical relationships studied extensively in algebra. They can be considered rules that relate the input numbers to the output numbers. For example, the data table shows the Double the Number rule with input and output numbers.

pages 235–236, 349, 352