T
tans
The seven shapes in a tangram set.
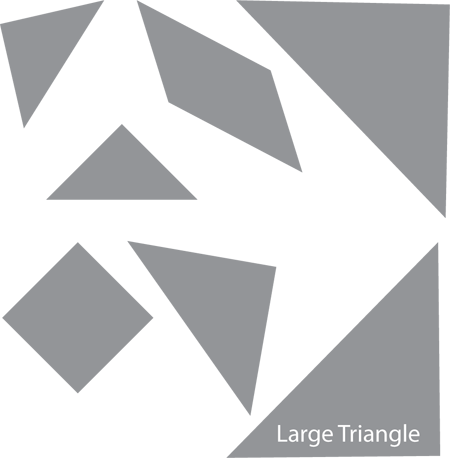
pages 303–304, 305–306
tangram
A type of geometric puzzle made with tans.
pages 303–304, 305–306
tens
Our number system is based on ten digits (numbers). Using the ten digits, a number can be written. The place where each number is written tells its value. The second place or column from the right is called the tens place. One ten or group of ten is equal to ten ones. For example, in the number 762, the 6 represents the quantity of six tens or sixty. Use 6 skinnies to show 6 groups of ten.
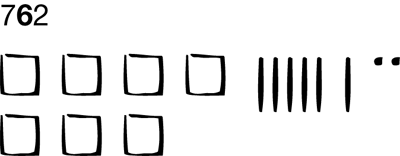
pages 19–20, 47, 60, 70, 71–77, 78–83, 126–127, 130–132, 142, 156, 161, 168–183, 234–236, 367, 369–371
thinking-addition strategy
A strategy for subtraction that uses a related addition problem. For example, 15 − 7 = 8 because 8 + 7 = 15.
page 42
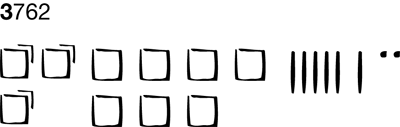
thousands
Our number system is based on ten digits (numbers). Using the ten digits, a number can be written. The place where each number is written tells its value. The fourth place or column from the right is called the thousands place. Ten groups of one hundred equal one thousand. For example, in the number 3762, the 3 represents the quantity of 3 groups of one thousand or three thousand. Use 3 packs to show three groups of one thousand or 3000.
pages 78–83, 130, 168–183
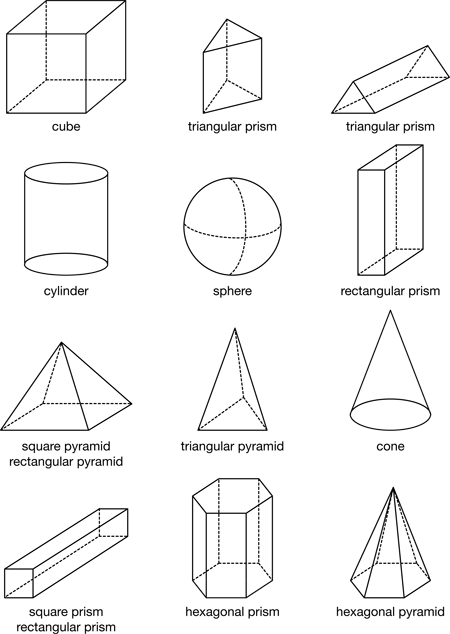
three-dimensional (3-D)
An object that has length, width, and depth, like objects in the real world.
pages 314–315
TIMS Laboratory Method
A method used to organize experiments and investigations. It involves four phases: draw, collect, graph, and explore. It is a way to model, analyze, and interpret a complex situation.
pages 9–10, 103
ton
Unit used to measure mass in the U.S. Customary System. A ton is equal to 2000 pounds.
trading
Regrouping or exchanging one item for another. For example, when using the Fewest Pieces Rule, if you have 12 bits, you trade 10 bits for one skinny.
(See also fewest pieces rule.)
pages 74, 79, 92, 138, 142, 159–160, 161–162, 165, 168–183
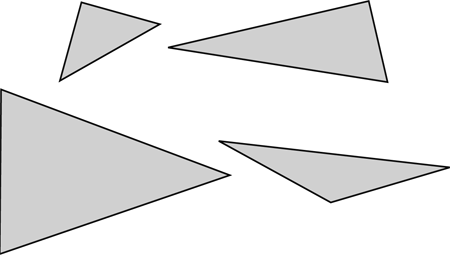
triangle
A polygon with three sides.
pages 214, 294–295, 304–305, 307–309, 314, 321
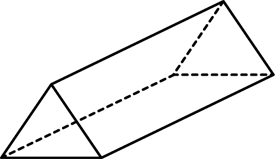
triangular prism
A prism with triangular bases.
pages 314, 318
triangular pyramid
A pyramid with a triangular base.
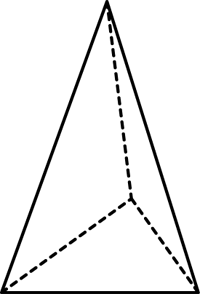
pages 317, 321
true number sentence
A number sentence where both sides of the equation are equal.
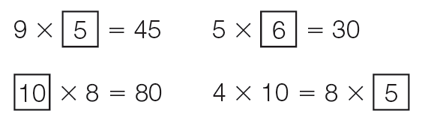
page 85
turn
To move a figure around a point.
(See also rotation.)
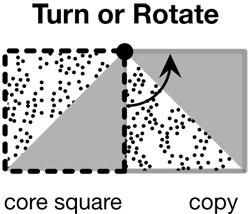
page 308
turn-around fact
Addition or multiplication facts that have the same numbers but in a different order (e.g., 3 + 4 = 7 and 4 + 3 = 7, 3 × 4 = 12 and 4 × 3 = 12).
(See also commutative property.)
pages 202, 204–205
turn-around rule
A term used to describe the commutative property of addition (e.g., 4 + 6 = 6 + 4) and multiplication (e.g., 4 × 6 = 6 × 4).
(See also commutative property.)
pages 202, 204–205
two-dimensional (2-D)
A shape having length and width but no thickness.
pages 314–315
two-pan balance
A tool for measuring the mass of an object by balancing the object in one pan and a number of standard masses in the other pan.
(See also equal-arm balance.)
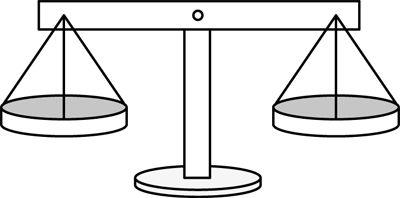
pages 348–350