S
sample
A smaller group or part of a population.
pages 8–11, 12, 13–14, 43
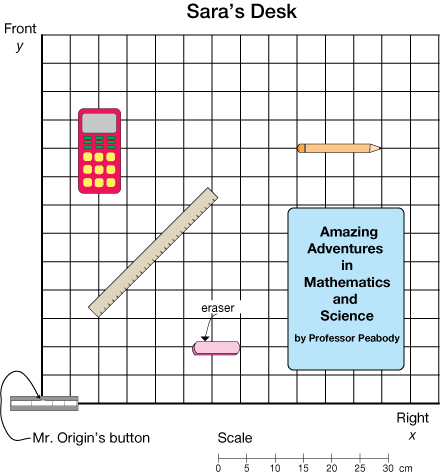
scale map
A map drawn to a certain scale. For example, on Sara's desk every square represents 5 centimeters.
pages 328, 347
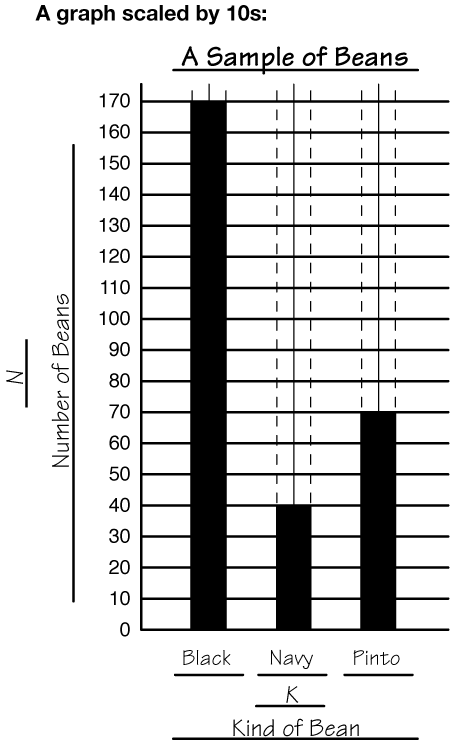
scaled graph
A graph where the intervals on the vertical axis increase by the same amount. When a graph is scaled by a value other than 1, it is understood that there are values between each of the points on the vertical axis.
side
The edge of a polygon.

pages 100, 210, 305, 307–309, 310–311, 318, 319–320
skeleton of a three-dimensional shape
A skeleton is a model of a polyhedron or three-dimensional shape that represents the edges and vertices. Connect drinking straws with paper clips to make a skeleton of a shape.
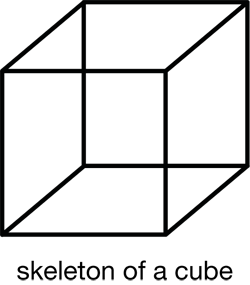
pages 316–318, 320
skinny
One of the base-ten pieces that is often used to represent 10. The block is a 10 × 1 × 1 arrangement of bits.
(See also base-ten pieces.)
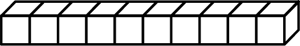
pages 70, 71, 73, 79, 138, 142, 159, 161–162
skip counting
Counting by a number that is not 1 using the same amount each time. For example, skip counting by 3 gives the multiples of 3. The multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, etc.
pages 55, 152, 199–200, 237–238, 370
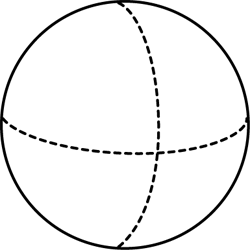
sphere
A three-dimensional object shaped like a ball. Every point on the shape is the same distance from the center. Because a sphere is not a polyhedron, it does not make sense to talk about its faces, vertices, and edges. An ordinary sphere does not have edges or vertices.
square
A polygon with four equal sides and four right angles.
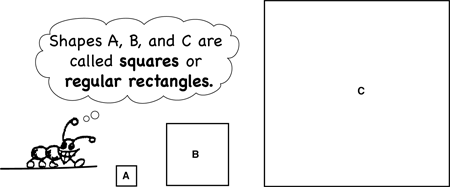
pages 99–100, 101, 294–295, 305, 307–308, 313–314, 316, 319–320, 321–322, 364, 370
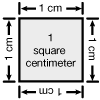
square centimeter
The area of a square that is 1 cm long on each side.
pages 100, 112, 121, 129–130, 135
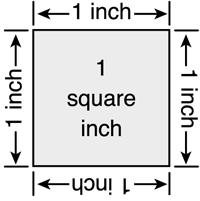
square inch
The area of a square that is one inch long on each side.
page 101
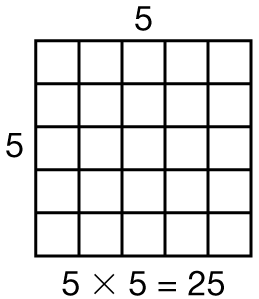
square number
A square number is made by multiplying a whole number by itself. For example, 25 is a square number since 5 × 5 = 25. A square number can be represented by a square array with the same number of rows as columns. A square array for 25 has 5 rows of 5 objects in each row or 25 total objects.
pages 100, 240, 242
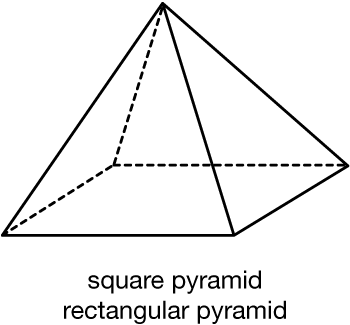
square pyramid
A pyramid with a square base.
pages 316–317, 321
standard form
Writing a number using one digit for each place value (e.g., 457 is standard form for 400 + 50 + 7, which is expanded form).
pages 130–132
standard mass
A set of objects used to measure the mass of an object. They often come in a set with masses that are easy to add together, usually 1 g, 10 g, 100 g, etc. They are often used with a two-pan balance.
page 350
strategy
A method or plan for solving a problem.
pages 16–18, 42, 45, 47–48, 49, 94, 97, 123–124, 126–128, 133, 134, 136, 139, 144–145, 152, 156–157, 166–167, 185, 199–200, 205–206, 208, 212, 242, 243, 296, 404
subtract/subtraction
The operation of finding the difference between two or more numbers (e.g., 45 − 7 = 38).
pages 40–45, 46, 47–48, 49–50, 126, 150–154, 155–157,158–160, 161–163,164–167, 168–183, 184–187, 188
sum
The answer to an addition problem.
pages 19, 21–23, 24–39
survey
A survey is a method of collecting data from a sample population. Usually surveys are used to describe a characteristic of the population sample. For example, the students in the class were asked to name their favorite food. From that information, you might be able to tell what is the most common favorite food.
switching numbers
The mathematical rule that says the order in which we add numbers in a number sentence does not matter.
(See also commutative property of addition.)
page 19
symmetry
A shape with symmetry is made of parts that are the same shape and size. The congruent parts can be facing each other (line symmetry) or be turned around a point (turn symmetry). For example, if you fold a shape in half, and the two sides line up perfectly, the shape has line symmetry.
pages 307, 309