A
acre
A measure of land equal to 43,560 square feet.
page 223
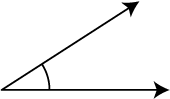
acute angle
An angle that measures less than 90°.
pages 369–372, 374, 379, 381, 390–392, 395, 399–400, 403
acute triangle
An acute triangle has three acute angles.

pages 400, 403, 422
addition
The operation of finding the total of two or more numbers. For example, 45 + 7 = 52.
pages 128–136, 152–153
all-partials method
A paper-and-pencil method for solving addition and multiplication problems. Each partial product or sum is recorded on a separate line. (See also partial product.)

pages 158–159, 281, 285–287, 492–497, 501, 503, 505–507, 547
analyze
To examine or study closely.
pages (data) 38–39, (shapes) 425–426
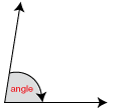
angle
The amount of turning between two rays that have the same endpoint.
pages 368–372, 378–383, 384–395, 396–404, 405–406
arc
A curved line that shows the turning of an angle. Sometimes the arc has an arrowhead to show the direction of the turn.
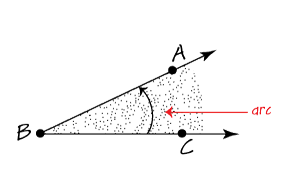
page 381
area
The area of a shape is the amount of space it covers, measured in square units.
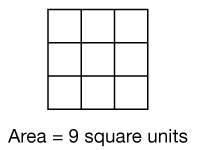
pages 52–53, 61–62, 63–64, 348, 544
array
An arrangement of elements into a rectangular pattern of (horizontal) rows and (vertical) columns.
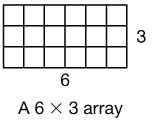
pages 72, 161–162, 547
associative property
The change in grouping of three or more addends or factors does not change their sum or product. (See also grouping rule.)
| Addition | Multiplication |
| (2 + 3) + 5 = 2 + (3 + 5) | (4 × 5) × 10 = 4 × (5 × 10) |
| 5 + 5 = 2 + 8 | 20 × 10 = 4 × 50 |
| 10 = 10 | 200 = 200 |
average
A number that can be used to represent a typical value in a set of data. (See also mean, mode, and median.)
pages 13–19, 40–41, 42–49, 169–176, 177–183