O
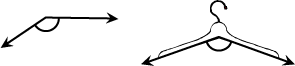
obtuse angle
An angle that measures more than 90°.
pages 369–372
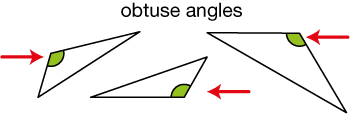
obtuse triangle
An obtuse triangle has one obtuse angle.
pages 400, 422
odd number
Numbers that are not multiples of 2 (1, 3, 5, 7, etc.) are called odd numbers.
page 68
ones period
The sequence of digits in the ones place, the tens place, and the hundreds place. In the number 456,789,987 the ones period is in bold type.

pages 220–221, 230
operation
A process that takes two numbers and results in a third. This is called a binary operation. For example, addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are operations.
pages 107, 252–256
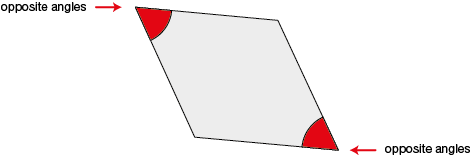
opposite angles
opposite sides
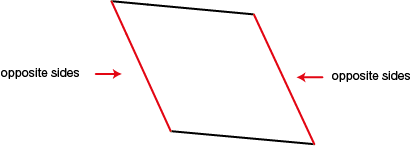
page 420
order of operations
A way to clarify which math procedures should go first in a math sentence that has more than one operation. 1. Do calculations in parentheses first. 2. Do all multiplications and division in order from left to right. 3. Then do all additions and subtractions in order from left to right.
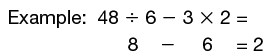
pages 252–256
ordered pair
A pair of numbers that gives the coordinates of a point on a grid in relation to the origin. The horizontal coordinate is given first; the vertical coordinate is given second. For example, the ordered pair (5, 2) tells us to move five units to the right of the origin and 2 units up.
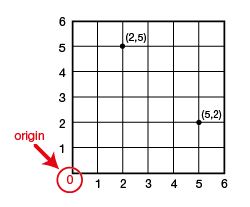
pages 36–39, 57, 187, 190, 195, 248–249, 476, 479, 561–562, 573–574
origin
The point at which the x-axis (horizontal) and y-axis (vertical) intersect on a coordinate plane. The origin is described by the ordered pair (0, 0) and serves as a reference point.
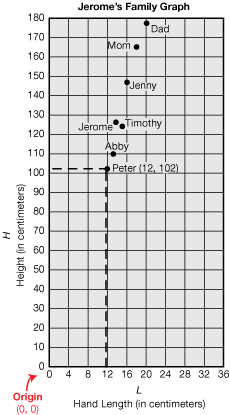
page 37
ounce
A unit for measuring equal to 
pages 273, 330, 489–491
output
The information that comes out or results from performing a function.

pages 208–211, 569–570, 577