M
manipulated variable
The variable with values known at the beginning of the experiment. The experimenter often chooses these values before data collection. It is often called the independent variable.
pages 185–186, 475–476, 561–562, 573
mass
The amount of matter in an object.
pages 47–49, 571–576
mean
An average of a set of data values that is found by adding the values and dividing by the number of values.

pages 169–176, 177–183, 249
measurement error
The unavoidable error that occurs due to the limitations inherent to any measurement instrument.
median
An average of a set of data values that is found by identifying the middle value. For a set with an odd number of data arranged in order, it is the middle number. For an even number of data arranged in order, it is the number halfway between the two middle numbers.

pages 13–19, 40–41, 42–49, 169–176, 182–183, 194–195, 249
megabit
A base-ten model that is a cube with an edge of length 100 cm. It represents 1,000,000 since it has a volume of 1,000,000 cubic cm.
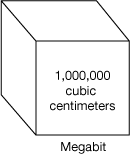
pages 228–230
meniscus
The curved surface formed when a liquid creeps up the side of a container (for example, a graduated cylinder).
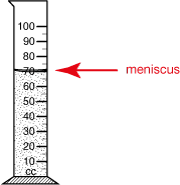
pages 556, 558
mental math
Mental math refers to any strategy that does not rely on a fixed computational algorithm, but involves the flexible use of operations to simplify problems (e.g., modeling a problem with coins or thinking of 99 × 4 as 100 × 4 − 4). While mental math strategies lend themselves to efficient mental computations, they may still involve intermediate calculations on paper or use of manipulatives, as strategies are developed.

pages 92–96, 104–105, 132, 134, 136, 142–143, 157, 160, 161–162, 530–534, 545
meter
A unit of length in the metric system. A meter is 100 centimeters or a little more than 39 inches.
pages 184, 189, 448–453, 454–455, 467, 471, 473, 475–476
miles per hour (mph)
How many miles traveled in one hour. It is usually the average speed for time traveled.
pages 275, 289
mililiter
A measure of capacity in the metric system that is the volume of a cube that is one centimeter long on each side.
pages 566–568
millions period
The sequence of digits (if any) in the millions place, the ten millions place, and the hundred millions place. In the number 456,789,987, the millions period is in the bold type.

pages 220–221, 230
mixed number
Mixed numbers are made up of a whole number and a fraction,
e.g., 2
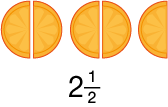
pages 320, 329, 464
mode
An average of a set of data values that is found by identifying the value that appears most frequently. Sometimes that number is used to represent the whole data set.
pages 13–17
multiple
The products of a number and another number. For example, 15, 25, and 40 are multiples of 5. A number is a multiple of another number if it is evenly divisible by that number. For example, 12 is a multiple of 2 since 2 divides 12 evenly.
pages 68, 70–71, 80–81, 88–89
multiples of ten
The products of ten and another number. For example, 20, 30, 40, and 100 are multiples of ten.
pages 264–270, 498, 530