F
fact family
Related math facts, e.g., 3 × 4 = 12, 4 × 3 = 12, 12 ÷ 3 = 4,
12 ÷ 4 = 3.
pages 72–78, 216–217
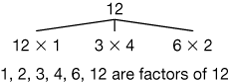
factors
The numbers that are multiplied together to get a new number. In the problem 3 × 4 = 12, 3 and 4 are factors of 12.
pages 79–83, 88–89, 90–96, 97–100, 257–258, 264–267
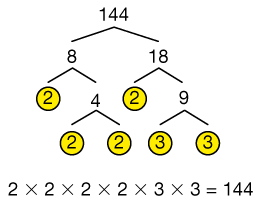
factor tree
A diagram that shows the prime factorization of a number.
pages 98–100
feet
Unit used to measure length in the U.S. Customary System. One foot is equal to 12 inches or 30.48 centimeters.
pages 103, 144–145, 164, 250, 538–540
Fewest Pieces Rule
Using the least number of base-ten pieces to represent a number.
(See also base-ten pieces.)
pages 113, 129, 131
fixed variable
Variables in an experiment that are held constant or not changed.
page 186
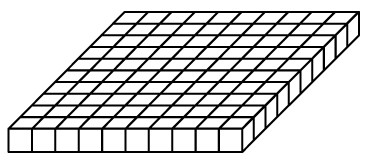
flat
One of the base-ten pieces that is often used to represent 100.
(See also base-ten pieces.)
pages 108–115, 133, 137–139, 228–230, 266, 456–457, 459–460, 467–470, 472
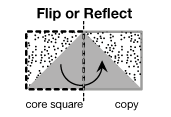
flip (or reflection)
A motion of the plane in which a figure is reflected over the line so that any point and its image are the same distance from the line.
pages 412–418, 428, 443
fluid ounce
A unit for measuring liquid equal to 
fraction
A number that is a part of a whole that can be written 





pages 297–366, 454–456, 459–462, 466–473
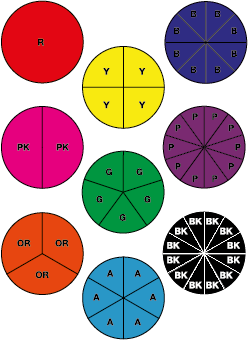
fraction circle pieces
Circles divided into equal sections to show various fractions.
pages 322–331, 464–465
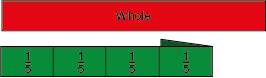
fraction strips
Strips of paper divided into equal sections to show various fractions.
pages 298–303, 304–308, 309–314
friendly numbers
Numbers that are easy to calculate to help find a reasonable estimate.
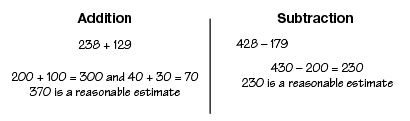
front-end estimation
Estimation by looking at the left-most digit.
function (machine, table)
Functions are important mathematical relationships studied extensively in algebra. They can be considered rules that relate the input numbers to the output numbers. For example, the data table show the n × 2 rule with input and output numbers.

pages 207–211, 569–570, 577