S
sample
A part or subset of a population.
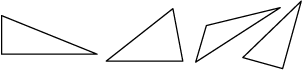
scalene
A triangle whose sides are all different lengths.
page 422
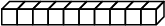
skinny
One of the base-ten pieces that is often used to represent 10. The block is a 10 × 1 × 1 arrangement of bits. (See also base-ten pieces.)
pages 108–109, 112, 115, 228–230, 470–471
skip counting
When you skip count, you say the multiples of a number. For example, skip counting by 3 gives the multiples of 3. The multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, etc.
pages 68, 70, 78, 260, 262, 456, 499
slide (or translate)
A way of moving an image while keeping its orientation the same (i.e., without flipping or rotating it).
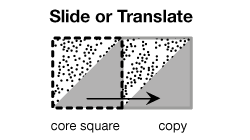
pages 412–418, 428
square
A polygon with four equal sides and four right angles.
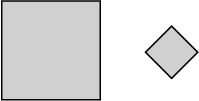
pages 53, 69, 368, 407–411, 412–414, 423, 428, 429, 439
square inch
The area of a square with a side length of one inch.
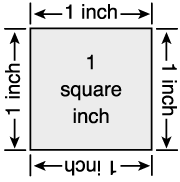
pages 53, 57, 62, 63–64, 66
square millimeter
The area of a square with a side length of one millimeter. One square centimeter is equal to 100 square millimeters.
square number
A number that is the result of multiplying a whole number by itself. For example, 36 is a square number since 36 = 6 × 6.
page 69
square root
The square root of a number n is the number whose square is n. The symbol for square root is √ . For example, the square root of 25 is 5, since 5 × 5 = 25. In symbols we write √25 = 5. The square root of 26 is not a whole number.
standard form
Writing a number using one digit for each place value (e.g., 457 is standard form for 400 + 50 + 7, which is expanded form).
page 113
straight angle
An angle that measures 180 degrees. The angle forms a straight line. Angle D is a straight angle made by two rays coming out of point D in opposite directions.
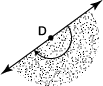
page 380
sum
The answer to an addition problem.
pages 150, 241
super bit
A base-ten model that is a cube of 1000 bits. It represents 1000.
(See also base-ten pieces.)
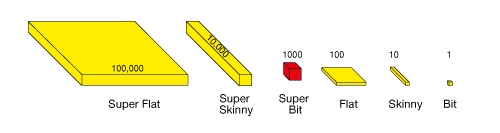
pages 228–230
super flat
A base-ten model that represents 100,000 bits. It is a 100 × 100 × 10 arrangement of bits. (See also base-ten pieces)
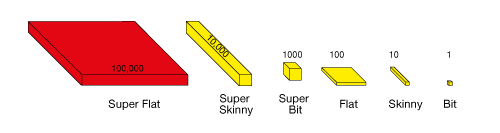
pages 228–230
super skinny
A base-ten model that represents 10,000 bits. It is a 10 × 10 × 100 arrangement of bits. (See also base-ten pieces)
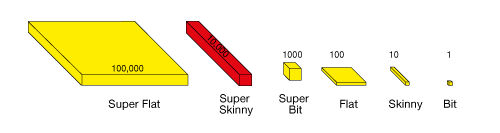
pages 228–230
survey
A survey is a method of collecting data from a sample population. Usually surveys are used to describe a characteristic of the population sample. For example, the students in the class were asked to name their favorite food. From that information, you might be able to tell what is the most common favorite food.
pages 19, 173