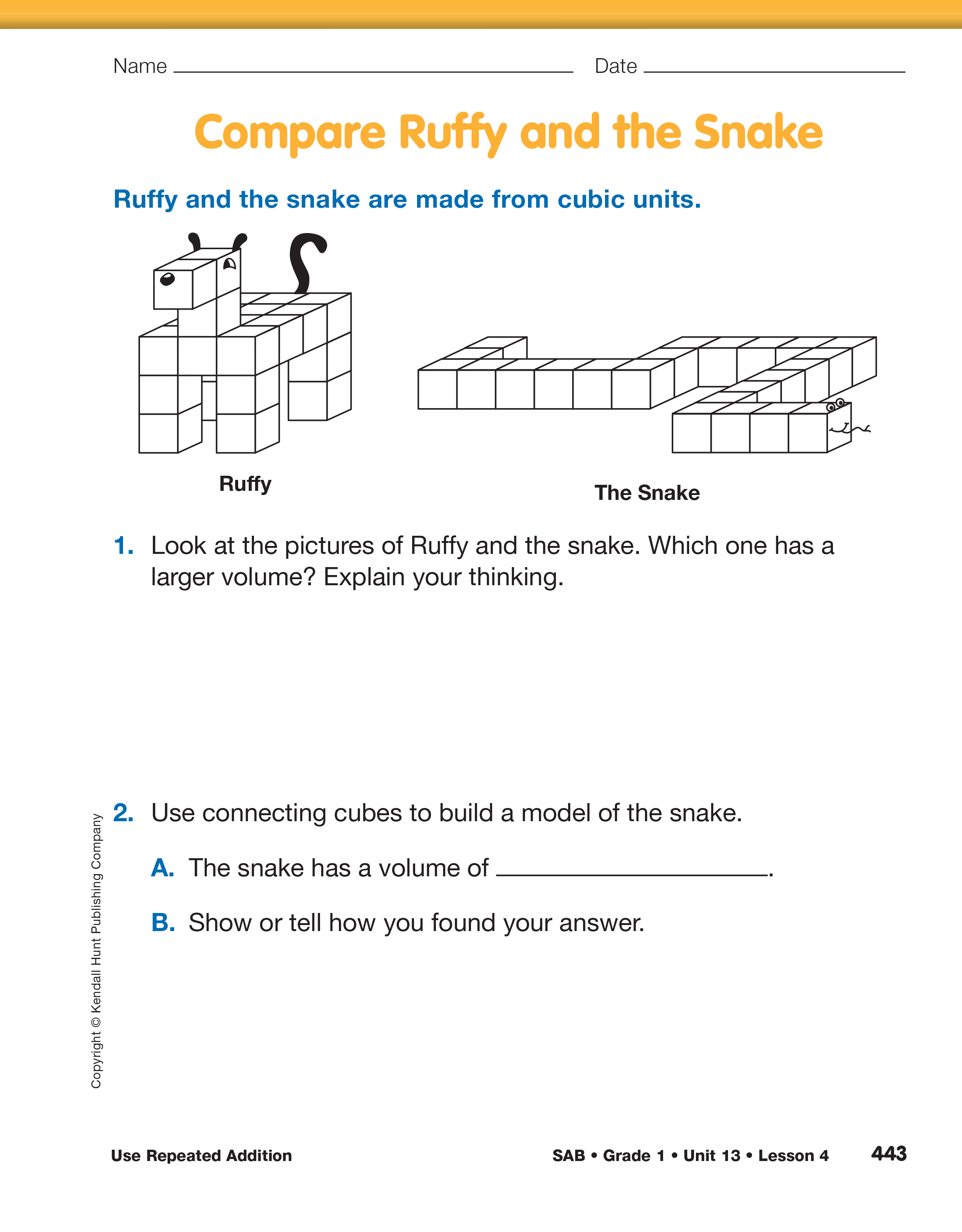
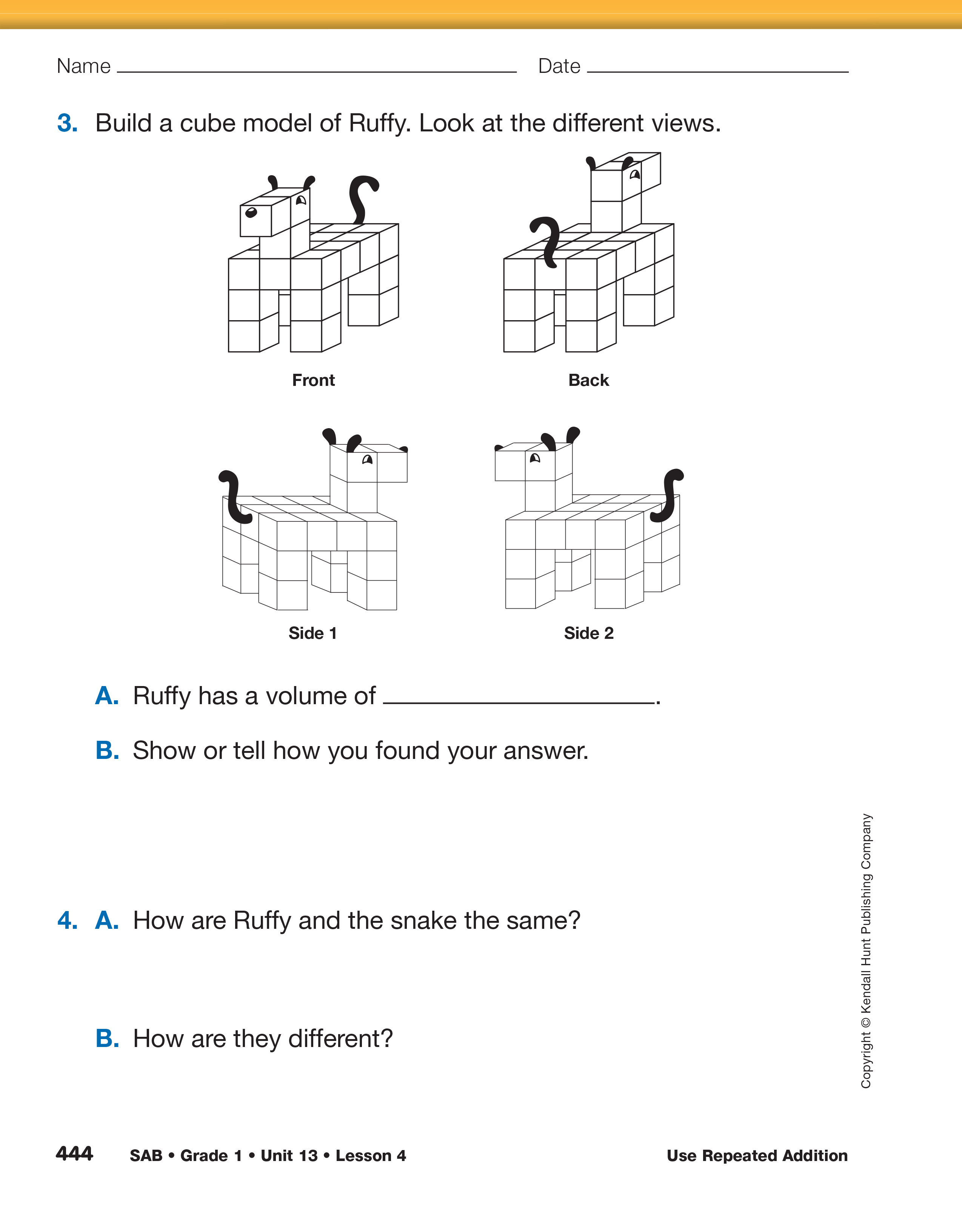
After reading and discussing A World of Cubic
Animals direct students’ attention to the Comparing
Ruffy and the Snake pages in the Student Activity
Book. Each student should work independently to
complete Questions 1–4. One purpose of this assessment
is to understand students’ reasoning process. For
example, do they understand that volume is not necessarily
greater because an object is longer or taller?
Some students may have difficulty building a model of Ruffy
from the pictures. Provide them with one of the models you
have prepared so they can focus on finding and comparing the
volumes of the shapes.
Use Compare Ruffy and the Snake pages in the Student
Activity Book to assess students’ abilities to solve problems
involving volume using skip counting and repeated addition
[E1], recognize that different shapes can have the same
volume [E5], and justify visual and spatial reasoning using
properties of volume [E6].
Targeted Practice. Six animals and Manuel are represented
as cube models in the story A World of Cubic Animals. Student
pairs can build and find the volume of Manuel and the cubic
animals illustrated in the story and record the information on
the class data table as shown in Figure 2. They can display their
models labeled with the name of the animal and the volume in
cubic units.

Figure 2: Volumes of characters in the A World of Cubic Animals story