Investigating Perimeter and Area
Est. Class Sessions: 2Developing the Lesson
Part 2: Investigating Perimeter and Area
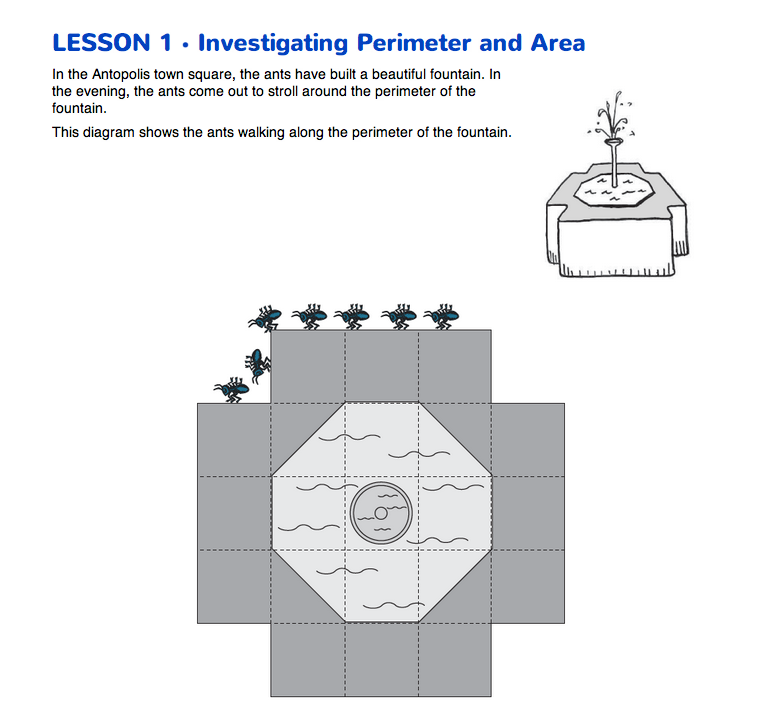
Area and Perimeter of the Fountain. Discuss the diagram of the fountain and the information on the Investigating Perimeter and Area pages in the Student Guide. Ask students to compare the small drawing of the fountain at the top of the page with the diagram to identify different parts of the diagram. The diagram is a “bird's-eye view” of the fountain in the drawing. The ants are walking along the perimeter of the fountain—its outside edge. Have students trace the perimeter of the fountain with their fingers. The lighter area around the center represents the water in the fountain.
Use Questions 1–4 to facilitate a discussion about area and perimeter.
Ask:
Have students demonstrate their methods for finding the perimeter and then ask:
After students have found the perimeter, ask:
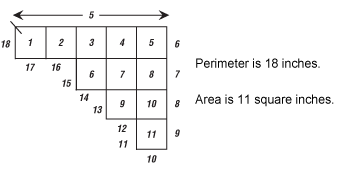
As students find each measurement, emphasize the use of the correct unit of measurement. The perimeter should be measured in inches. The area should be measured in square inches. Some students mix up the concepts of perimeter and area. Calling attention to the correct unit of measurement facilitates differentiation between the two concepts.
Practice with Tiles. If students need more experience finding perimeter and area, present more examples by building shapes made of square-inch tiles on a class display of the Square-Inch Grid Paper Master. Ask student volunteers to count the inches around the perimeter of each shape and count the number of square-inch tiles to find the area. Ask another volunteer to use a ruler to measure the length of the edges. It is also important to have students build their own shapes. Ask students to do so, and ask their partner to verify the area and the perimeter.
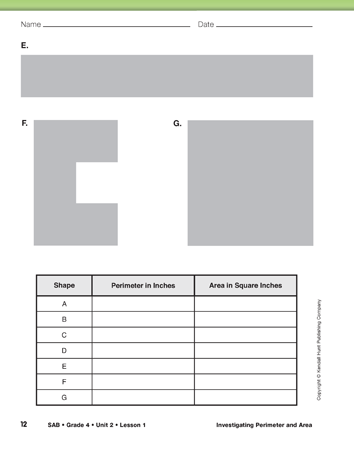
Practice with Irregular Shapes: Use the Perimeter-Area Puzzles pages in the Student Activity Book to give students independent practice finding perimeter and area. Suggest to students that when finding perimeter, they first measure the sides with a ruler. They can then place square-inch tiles over the silhouettes of the polygons and count edges to verify their measurement. They can also use the square-inch tiles to find area.