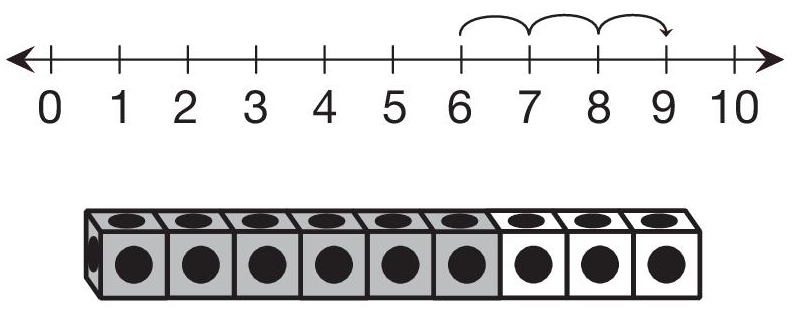
Connect Representations of
Numbers. To conclude the lesson, help students make connections
between the number representations they have been using. See
Figure 5. Each student will need 20 connecting cubes and the
number lines on his or her desk. Direct students' attention to
the last two problems on the Math Hoppers pages.
- A math hopper started at 6 and moved forward 3
units on the number line. Where did it land? (9)
- Can you solve the same problem using your
connecting cubes? Do you think the answer will be the same?
(yes)
- Start with 6 cubes and add 3 more cubes to the
train. How many cubes do you have altogether? (9)
- How do you know? (Possible response: I started
at 6 and counted on 3 more, 7, 8, 9.)
- How can we check this answer using the number
line? (Students point to 6 on their desk number lines as you
do the same on the classroom number line. Move 3 units forward
and count on 7, 8, 9.)
- The last math hopper on your page started at 8
and moved forward 2 units. Where did it land? (10)
- Show us how to solve this problem another way
using cubes or the number line. (Possible responses: Start
with 8 cubes and add 2 more to the train. Count on 9, 10. Or,
start at 8 on the number line, move 2 units forward and count
9, 10.)
- How are these problems different? How are they
alike? (We used different tools to solve them—cubes, number
lines, and math hoppers. They are alike because we are
starting at a number and counting on and we get the same
answer no matter what tool we use to solve them.)
- We need to choose good tools when we solve
problems. Which tool did you like to use best today? Why?
(Responses will vary.)