Which Picks Up More?
Est. Class Sessions: 4–5Developing the Lesson
Part 3. Represent and Analyze the Area Data
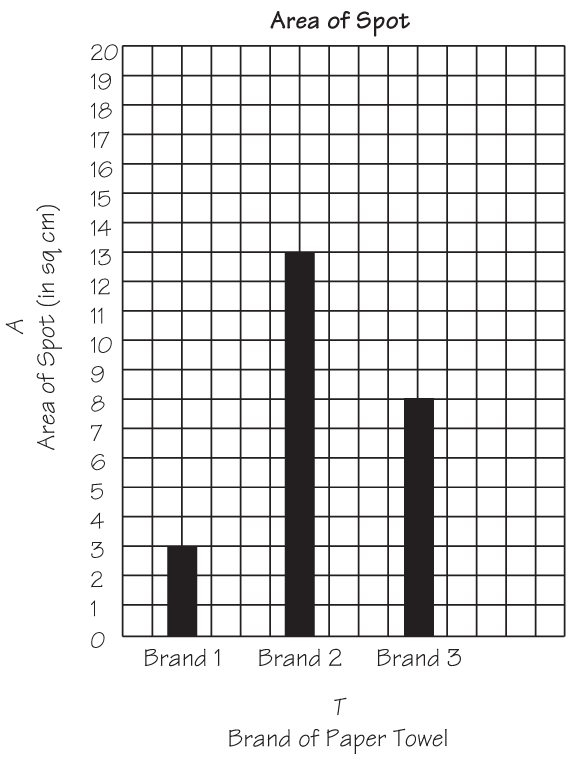
Make a Graph. In Question 4, students are asked to make a scaled bar graph. Display a copy and distribute copies of the Centimeter Graph Paper Master. Model how to label, scale, and draw bars on this type of graph paper.
Ask:
Help students decide on an appropriate scale for the vertical axis by looking at the spot with the largest area. If the area is larger than 20 square centimeters, students will have to scale the axis by twos. Ask each group to graph their data on their bar graph (Question 4).
Use the Graph to Make Predictions and Generalizations. Ask groups to discuss and answer Questions 5–9 in the Student Activity Book using the graph they just made.
Ask: