Skip Counting
Estimated Class Sessions: 1Developing the Lesson
Read and Discuss Two Ways to Count to Ten. Read Two Ways to Count to Ten by Ruby Dee as an introduction to skip counting. This book retells a Liberian folktale about jungle animals competing in a spear-flinging competition. To win, the contestant must fling a spear into the air and count to ten before it hits the ground. The winner used skip counting to count to ten before the spear hit the ground.
Questions to ask the students after reading the story:
Simulate Leopold’s challenge by dropping a sheet of paper and asking students to count to ten before it touches the floor. Ask students to first count by ones and then by twos.
Practice Skip Counting by Twos. There are a number of ways to practice skip counting. Skip counting is a key arithmetic skill students must learn and master. It helps students understand the concept of place value and develop mental math skills to do addition. Students need a lot of practice aloud and with various representations to formalize this understanding.
To initiate skip counting as a class, ask eight students to come to the front of the room and stand with their arms in the air. As you point to each arm, ask students to count by ones. Then begin again. This time as the class counts, tell students to whisper the odd numbers and say the even numbers loudly as you point to every arm: one, TWO, three, FOUR, five, SIX, seven, EIGHT.
Repeat a few more times, each time with the whispers becoming softer and the loud numbers becoming louder. Eventually, students should say only the loud numbers aloud and say the whispered number in their heads. Reinforce this by clapping on the even (loud) numbers. Emphasize that students are counting the second arm in each pair and are skipping the first arm, thus the term “skip counting by twos.”
Ask:
Repeat the count a third time, but this time point to and count every other arm (e.g., the second arm, the fourth arm, etc.). Practice skip-counting items in the room until students are comfortable with counting by twos.
Skip Count with Counters. Display an even number of connecting cubes. First have a student count them by ones. Then tell students you are going to count them by skip counting by twos. Have the class count with you as you separate out two at a time. Repeat with a different number of connecting cubes counting by ones and by twos. Emphasize that both methods of counting result in the same number.
Each time a set of cubes is counted, ask:
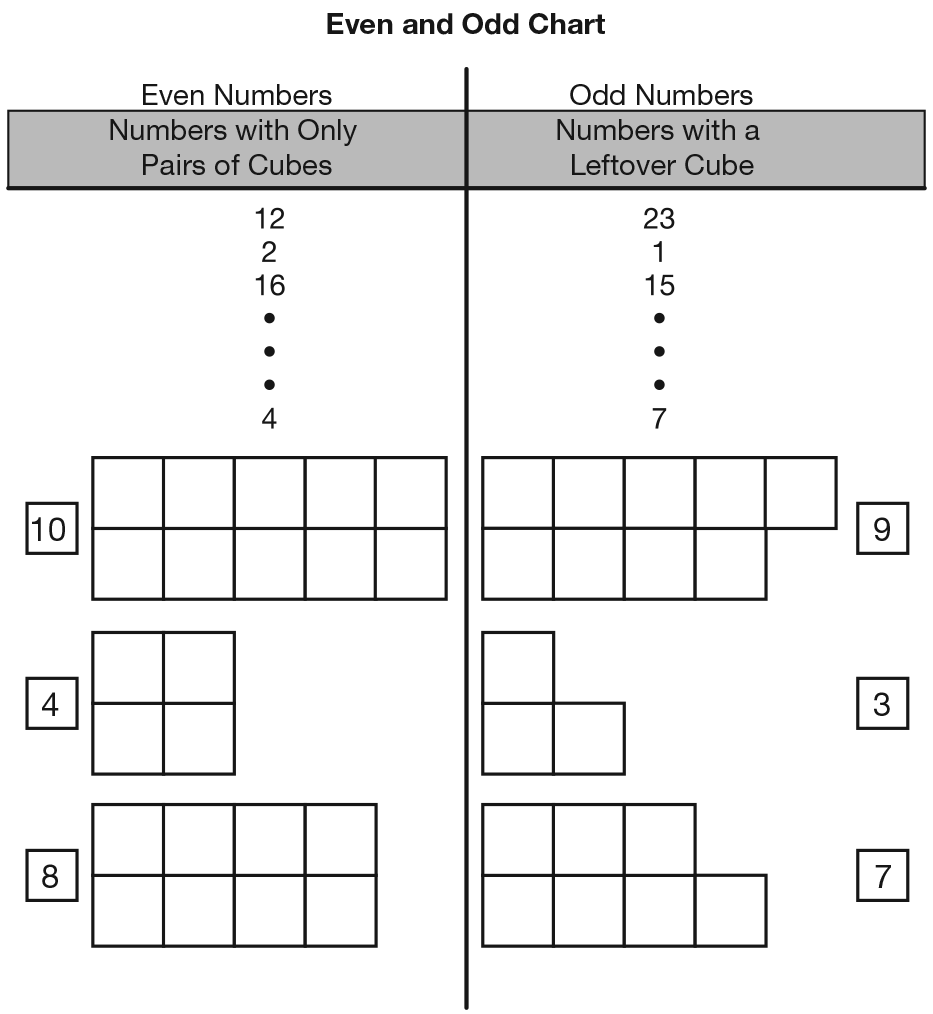
Skip Count with the Even and Odd Chart. Refer students’ attention to the Even and Odd Chart from Unit 4 on display. See Figure 1.
Ask:
Ask a student to demonstrate how to use the chart to skip count by two. Be sure to ask the student to start with the even column and count by two and start with the odd column and count by two.
Ask:
Skip Count with Number Lines. Ask students to focus on the class number line. Have students skip count by two as you point to the corresponding numbers on the number line. Gradually have students skip count to higher numbers using the number line for support. Use similar questions to discuss skip counting on the number line.
Ask:
Continue with other examples, using the class number line and numbers up to 50.
Skip Count Using a 100 Chart. Display the My First 100 Chart Master. Ask students to count by ones from one to thirty. As they count, write each number on the chart. When you get to ten, ask students where they think you should write eleven. Moving down a row and going to the far left box should remind them of the numbers on the calendar and the way they read books.
After recording the numbers, ask students to count from one to thirty a second time. This time, point to the even numbers and ask students to skip count by twos. Color the even numbers red to emphasize the numbers they should say and which ones they should skip.
Ask:
Skip Count with Calculators. Distribute calculators to every student. Explain that the calculator is a tool that can help them think about number patterns and can be used to check their calculations. Have students check the numbers colored red on the 100 Chart by having them start with 2 on the calculator and pressing + 2 =. The window should show 4. To continue skip counting by 2, press =. Each time the ”hot“ equal key is pressed, 2 is added.
Compare the calculator numbers to the numbers colored red on the chart.
Help students set up their calculator to add 2 starting at 1. Press: 1 + 2 = = =
Ask: