Students discuss the difference between regular and irregular shapes. They measure regular shapes to the nearest centimeter and then look for the relationship between side length and perimeter. A variety of tools and strategies are used to solve perimeter problems including making point graphs, using mental math to multiply and divide, and using patterns in data tables, graphs, and number sentences.
Content in this Lesson
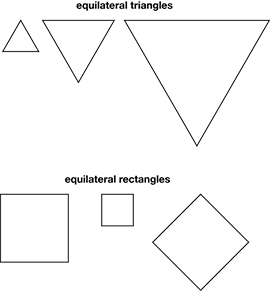
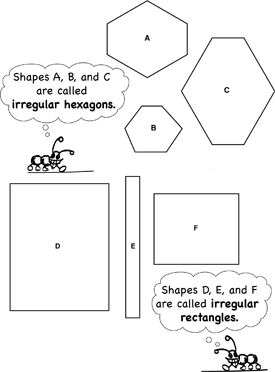
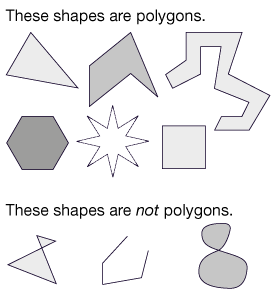
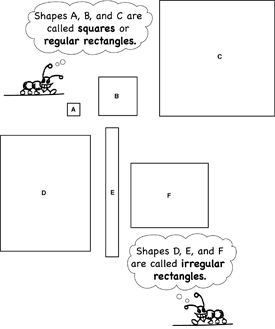
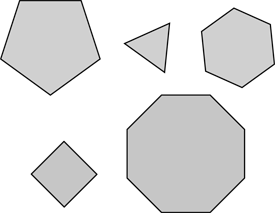
- Identifying regular and irregular polygons including triangles, rectangles, and hexagons.
- Finding the perimeter of regular polygons.
- Identifying and extending multiplicative patterns in graphs and tables [E1].
- Representing multiplicative patterns in graphs and tables [E2].
- Multiplying and dividing using mental math strategies [E3].
- Representing solution strategies for problems involving multiplication [E4].
- Representing solution strategies for problems involving division [E5].
- Making point graphs to model real-world situations [E6].
- Reading a table or point graph to find information about a data set [E7].
- Measuring to the nearest whole centimeter [E8].
- Checking work for accuracy with a second method [MPE3].
- Communicating solution strategies [MPE5].
Daily Practice and Problems O–T
Assessment in this Lesson
| Assessment | Expectation Assessed | Math Practices Expectation Assessed |
|---|---|---|
|
Walking Around Shapes Practice Menu |
|
|
|
Perimeter Page |
|
|
|
Walking Around Hexagons |
|
|
|
Professor Peabody's Shapes Data |
|