Workshop: Graphs and Averages
Est. Class Sessions: 1–2Before the Lesson
Review student work and progress from previous lessons to guide instructional decisions about the following Expectations:
| E6. | Find the median of a data set represented in a table, graph, or line plot. |
| E7. | Read a table or graph to find information about a data set. |
| E9. | Make predictions and generalizations about a data set using a median. |
For each of these Expectations, evaluate students' progress using the following questions as a guide:
| 1. | Which students are having particular difficulties meeting the Expectation? |
| 2. | Which students are making progress, but need additional practice? |
| 3. | Which students have already met the Expectation and are ready to extend their learning? |
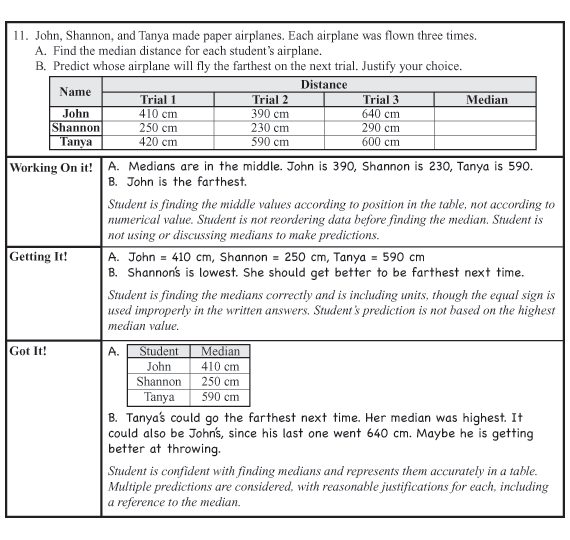
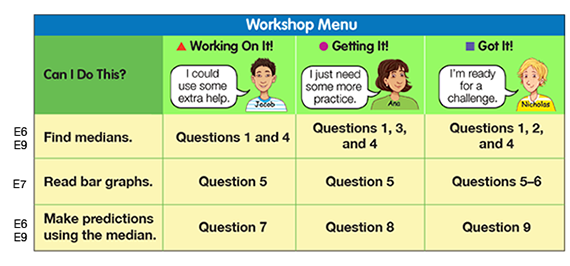
For example, you might look at student responses to Check-In: Question 11 in Lesson 3 to determine their progress in finding medians and reading tables and graphs to make predictions. Figure 1 shows samples of responses from 3 students, along with sample teacher thinking about each response. The levels of confidence (Working On It!, Getting It!, Got It!) correspond to those on the Workshop Menu on the Workshop: Graphs and Averages page in the Student Guide. See Figure 2. This review of student work then informs decisions about how to guide each student to choose the appropriate set of problems. Review the Graphs and Averages Workshop Menu in Figure 2 and in the Student Guide to orient yourself to the organization of the Workshop.
Students will self-evaluate to identify their levels of confidence with a particular concept and will complete the recommended problems from the Workshop Menu. Offer students guidance based on your observations and your review of their work. Students select and complete one set of problems from each row based on their confidence level with each type of problem (Working on It!, Getting It!, or Got It!). See the TIMS Tip for more about Workshop Menus.
Plan to organize the class into small groups or stations based on the problems they solve. Students can check each other's work and discuss solutions. Students may need to work with different groups as they work on different problem sets.