Units of Volume
Est. Class Sessions: 1Developing the Lesson
Estimate and Measure the Volume of a 1-liter Bottle.
Show students an empty 1-liter bottle and ask:
Discuss strategies for estimating the number of cubic centimeters in a 1-liter bottle. Ask students to work with a partner to choose and write down their best estimate for the number of cubic centimeters in a 1-liter bottle. After student pairs have recorded their estimates, distribute the materials you gathered for each student pair before the lesson: graduated cylinders, eyedroppers, containers of water, empty 1-liter bottles, and paper towels. Ask students to use the graduated cylinder to measure the volume of the bottle in cubic centimeters.
While groups are working, ask:
Compare student measurements by collecting them as they complete them. All student measurements should be close to 1000 cc. Check the process and calculations of measurements not within 10 cc of 1000 cc.
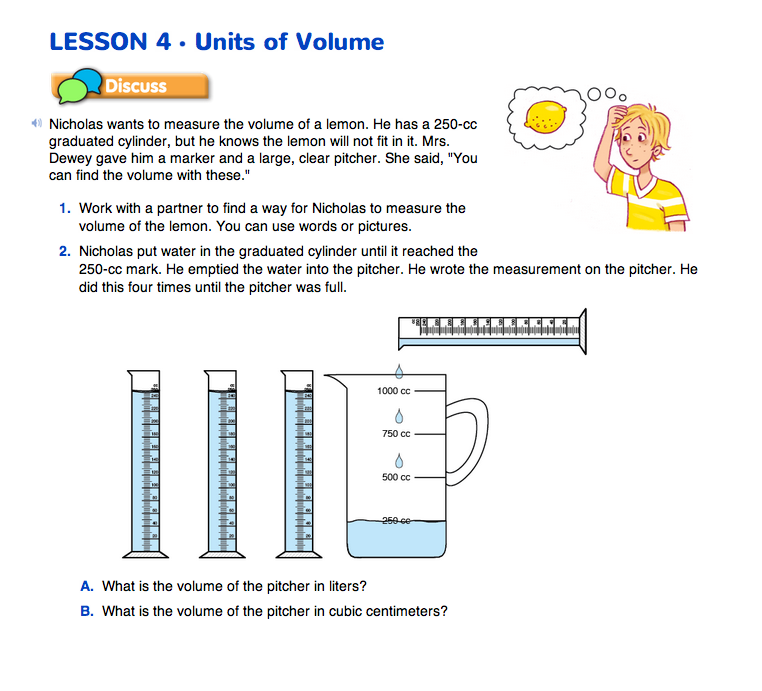
Estimate and Measure the Volume of a Lemon. Introduce Nicholas's problem in Question 1 on the Units of Volume pages in the Student Guide. Show the class a pitcher, a marker, a 250 cc graduated cylinder, and a lemon. Then ask student pairs to work together to develop a strategy for measuring the volume of a lemon.
Ask:
Discuss students' strategies:
Have the class choose two strategies that they think are accurate and efficient. Have volunteers find the volume of a lemon using each strategy and compare the results.
Ask pairs to answer Questions 2 and 3 to explore Nicholas's strategy for measuring the volume of the lemon. After students have had a chance to explore the questions on their own, review them as a class.
Explore Units of Volume. Summarize the unit relationships in Question 3 by asking the class to complete the following sentences:
1 liter = _________ cc (1000)
0.5 liter = _________ cc (500)
0.25 liter = _________ cc (250)
0.75 liter = _________ cc (750)
Discuss the relationship between cubic centimeters and milliliters by exploring Question 4 together as a class. Add this number sentence to the list above:
1 ml = 1 cubic centimeter (cc)
Use Questions 5–12 to reinforce the relationships between these units of measure. In Question 11, students are asked to compare milliliters and cubic centimeters to liters using benchmarks. In Question 12, students complete number sentences to compare milliliters and cubic centimeters to liters.