|
|
Daily Practice and Problems |
Lesson |
Homework |
Assessment |
Student Books |
Student Activity Book |
|
|
|
|
Teacher Resources |
Teacher Guide - digital |
|
|
|
|
Supplies for Students
1 self-adhesive note
centimeter ruler
calculator, optional
Supplies for Student Pairs
1 self-adhesive note
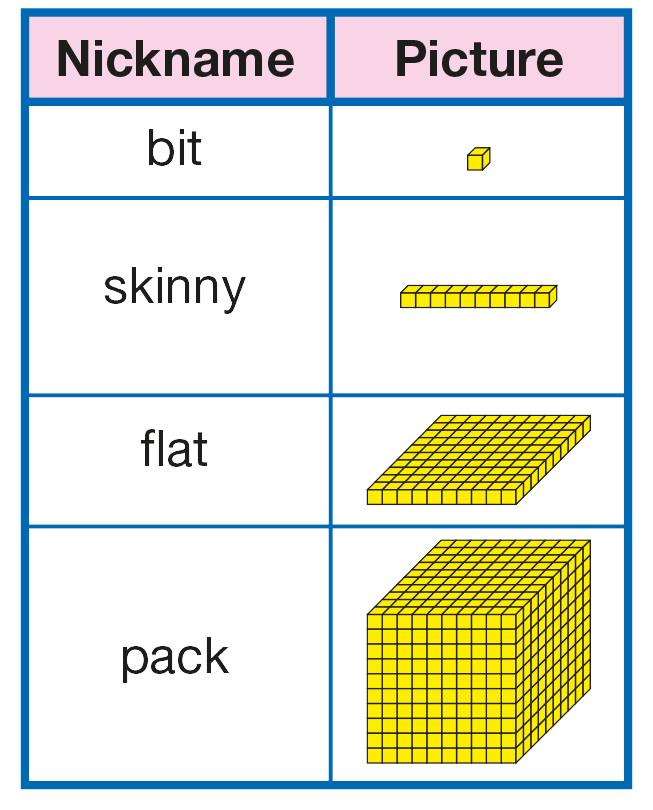
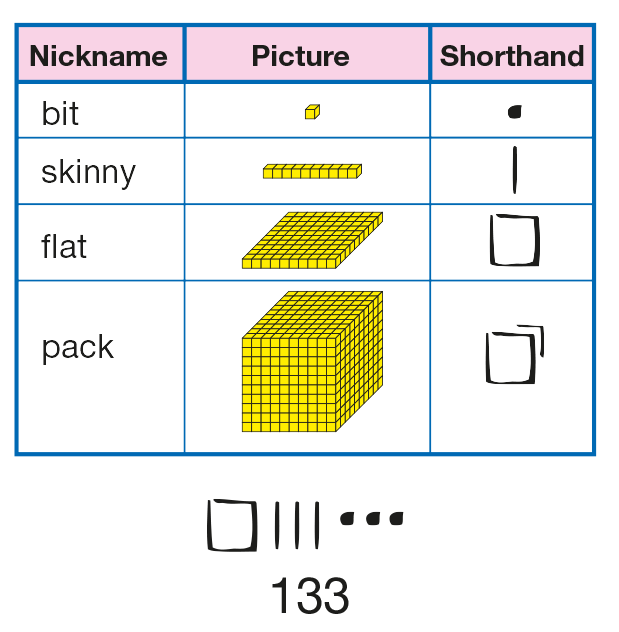
base ten pieces (about 30 bits and 10–15 skinnies)
clear plastic spinner or pencil with a paper clip
Materials for the Teacher
Display of Collection of Bits Master (Teacher Guide)
Display of Show Me the Number Spinners (Student Activity Book) Page 276
Display of Show Me the Number Recording Sheet (Student Activity Book) Page 277
Unit 6 Assessment Record
collection of base-ten bits, about 500
2 referent bags of 10 and 100 connecting cubes from Unit 5. See Materials Preparation.
2 referent bags of 10 and 100 base-ten bits. See Materials Preparation.
collection of about 50 skinnies placed in a "Skinnies Bank." See Materials Preparation.
resealable bags. See Materials Preparation.
chart paper
one larger or different-colored self-adhesive note
Materials Preparation
Prepare a Skinnies Bank. Gather a bag or box and about 30 skinnies for a Skinnies Bank.
Prepare Referent Bags of Bits. Place ten loose bits in a resealable bag and 100 loose bits in another
resealable bag.
Prepare Referent Bags of Connecting Cubes. If you do not have the referent bags from Unit 5, place ten loose
connecting cubes in a resealable bag and 100 loose connecting cubes in another resealable bag.
Prepare an Interval Chart. Draw an interval chart on a display. Students will place self-adhesive notes with
their estimates on this chart. See Figure 1.
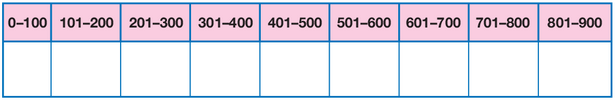
Figure 1: Interval Chart
TIMS Tip
Modify Interval Chart. If space is limited, you may omit the smaller or larger intervals on the Interval Chart. Make sure that the total
number of bits in the collection you are using will fall within the intervals you list. If you decide to do this activity with a larger or
smaller number of bits, change the interval chart accordingly.
Prepare Sets of Base-Ten Pieces. Before Part 2, prepare sets of base-ten pieces for each student pair. Place
about 30 bits and 10–15 skinnies in each container.
Prepare Spinners. Gather spinners or materials for spinners. If you do not have clear plastic spinners, students
can use paper clips and pencils. Straighten out one end of the paper clip, and place a pencil through the
curved end. Then put the point of the pencil on the center of the spinner, and spin the paper clip around the
pencil, using the straightened end as the pointer. See Figure 2.
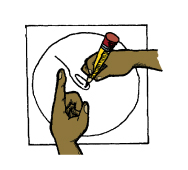
Figure 2: Using a pencil and paper clip as a spinner