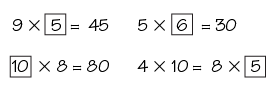In Part 1, students complete open number sentences using their multiplication tables and the Patterns for Remembering the Facts chart. In Part 2, students complete Function Machines involving multiplication. For Part 3, students read Cipher Force!, a story about a team of four superheroes and their sidekick. The superheroes—Multiply by Zero, Divide by Zero, Add Zero, and Subtract Zero—embody basic operations with zero. Several silly adventures show what happens when you use these operations with zero.
Content in this Lesson
- Completing open number sentences involving multiplication.
- Recognizing that the equal sign represents the relationship between two equal quantities.
- Using strategies to solve multiplication and division problems [E2, MPE2].
- Representing multiplication and division problems with number sentences [E1].
- Using the multiplication properties of 0 and 1 to solve multiplication problems [E3].
- Using turn-around facts to solve multiplication problems [E4].
- Demonstrating fluency with the multiplication facts for the 5s and 10s [E12].
- Using patterns in tables to solve multiplication and division problems [E5].
- Identifying and using properties and patterns in addition, subtraction, and multiplication with zero [E3] and [E5].
- Understanding why division by zero is impossible.
- Showing work [MPE5].
Daily Practice and Problems CC–FF
CC. Multiplication: 5s and 10s
Assessment in this Lesson
| Assessment | Expectation Assessed | Math Practices Expectation Assessed |
|---|---|---|
|
Multiplication with 5s and 10s |
|
|
|
DPP Item CC |
|