3-D Shapes
Est. Class Sessions: 2Developing the Lesson
Part 1. 3-D Shape Hunt
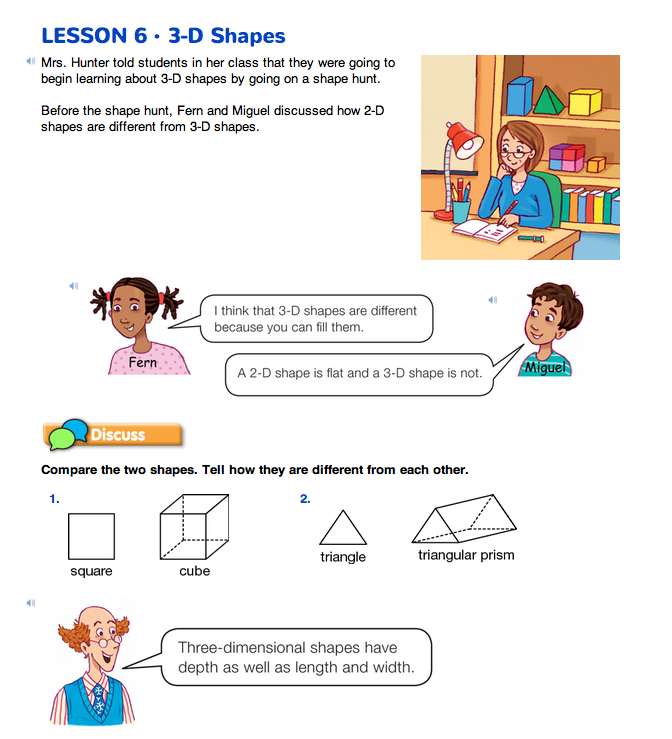
Identify Differences Between 2-D and 3-D Shapes. Explain that two-dimensional shapes can be drawn on a flat surface. You can illustrate this by drawing examples of a triangle, a circle, a square, and a rectangle. Remind students of two-dimensional shapes they learned about in previous lessons. Point out that three-dimensional, or 3-D, shapes are not flat because they have depth, as well as length and width.
Introduce 3-D Shapes. Read and discuss the vignette and Questions 1–2 on the 3-D Shapes page in the Student Guide.
Show students examples of each of three-dimensional shapes that you have gathered for this lesson.
As you introduce each shape, ask:
Continue to do the same for each shape you introduce.
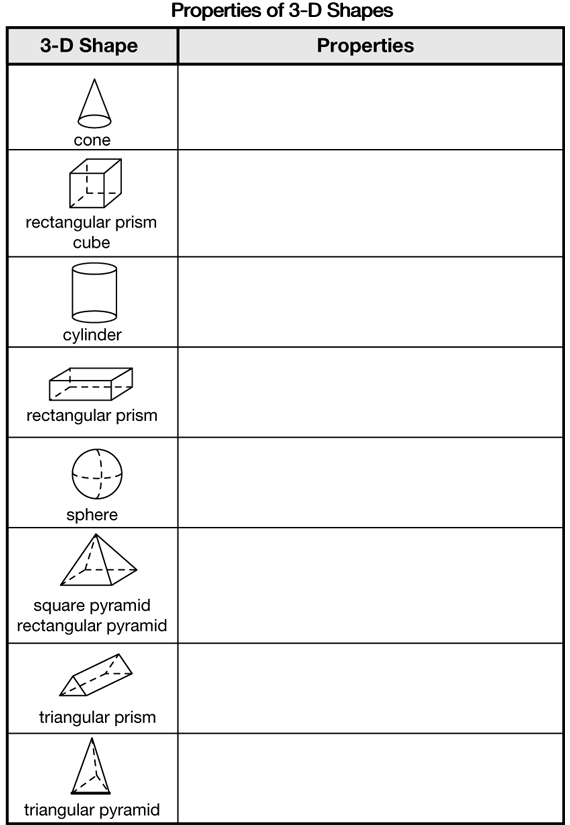
During the discussion use the terms cone, cube, cylinder, rectangular prism, sphere, square pyramid, triangular pyramid, and triangular prism. As you model the use of the mathematical vocabulary, most students will readily incorporate the new words into their everyday language. However, do not expect them to memorize the geometric terms. Students can invent their own terminology or use terms they already know, such as “box” for rectangular prism and “ball” for sphere.
When introducing different types of shapes, show various examples of each. Students need to see that all pyramids and prisms are not alike. For example, a triangular pyramid can have bases other than equilateral triangles and a rectangular pyramid can have a square base, as well as a nonsquare rectangular base. See Figure 2.
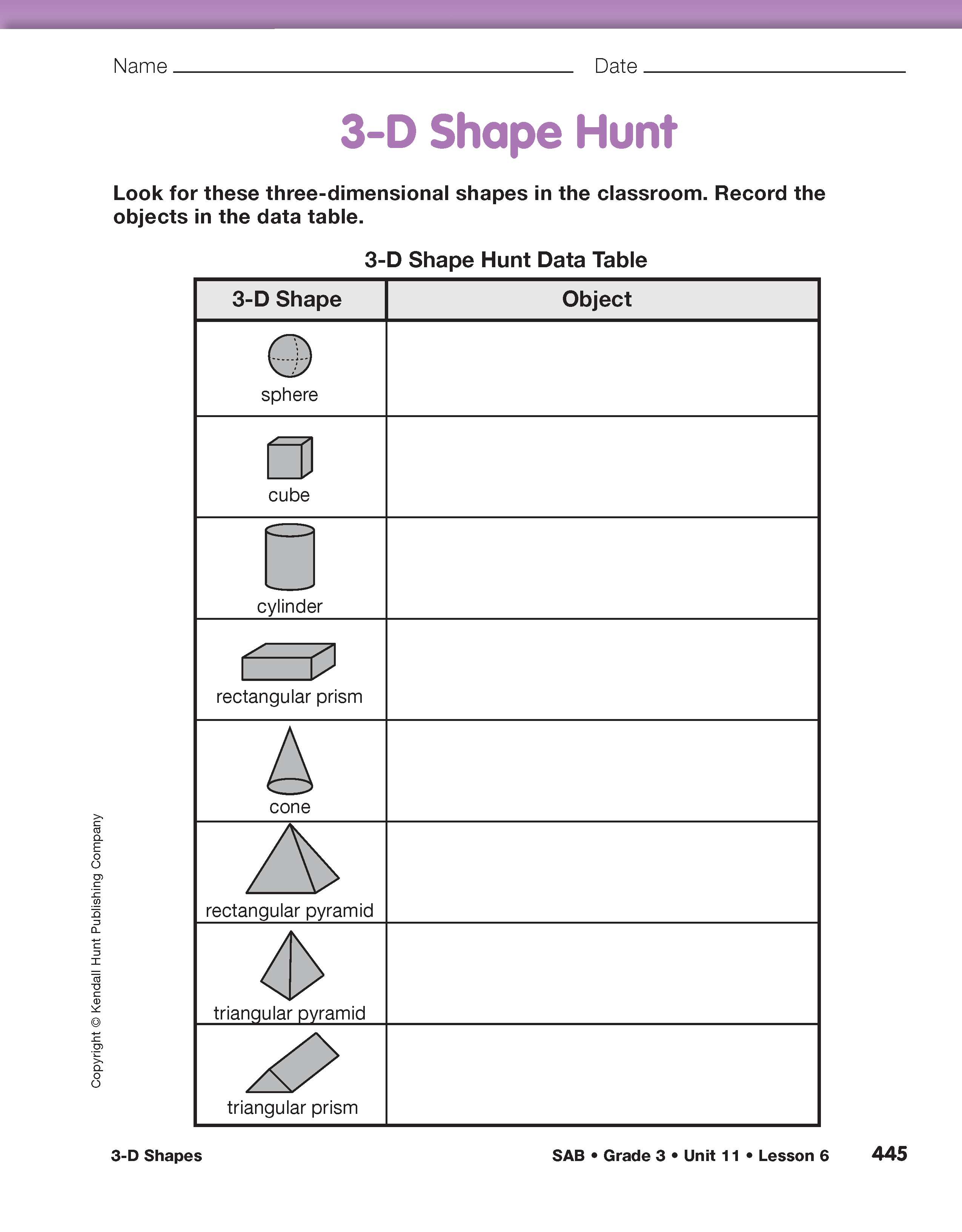
Next have student pairs preview the data table and the three-dimensional shapes illustrated on the 3-D Shape Hunt page in the Student Activity Book. Have them search the classroom for examples of each shape. Offer models of these shapes as a reference during the search. Tell partners to record the objects they find in the data table and record a few examples on a display of this page. Conclude this part of the activity by having students analyze the three-dimensional objects they identified.
Pose the following questions to prompt discussion: