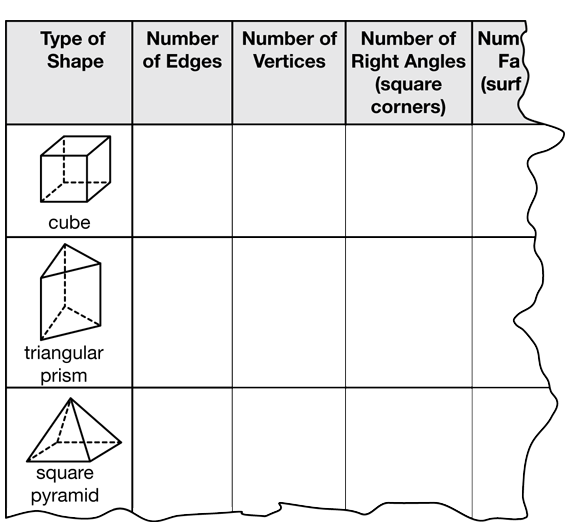
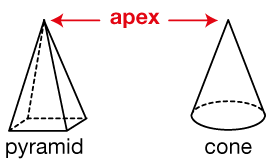
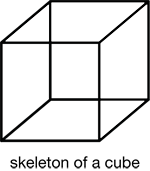
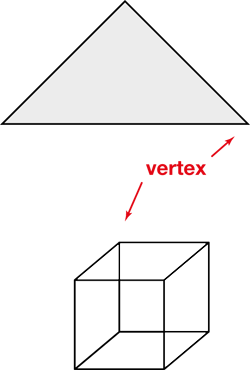
Students use plastic straws and chenille stems to construct skeletal models of three-dimensional shapes. They also identify the shapes' properties—the number of edges, vertices, and faces—of each shape they build. Then students manipulate their skeletal models to solve problems.
Content in this Lesson
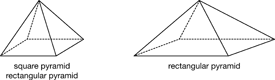
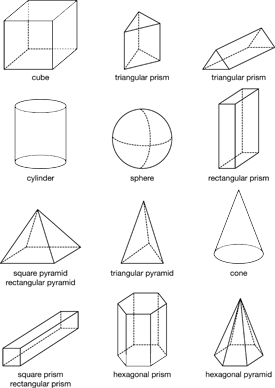
- Describing and analyzing three-dimensional shapes using their properties (e.g., number and shape of sides, number of edges, and number of corners) [E2].
- Identifying and constructing skeletal models of three-dimensional shapes using their properties [E3].
- Identifying congruent faces of shapes [E5].
- Justifying conclusions using geometric properties [E7].
- Using geometric concepts to solve problems.
Daily Practice and Problems W–Z
Assessment in this Lesson
| Assessment | Expectation Assessed |
|---|---|
|
Observe |
|
|
Triangular Prism |
|