Equivalent Fractions on Number Lines
Est. Class Sessions: 2–3Summarizing the Lesson
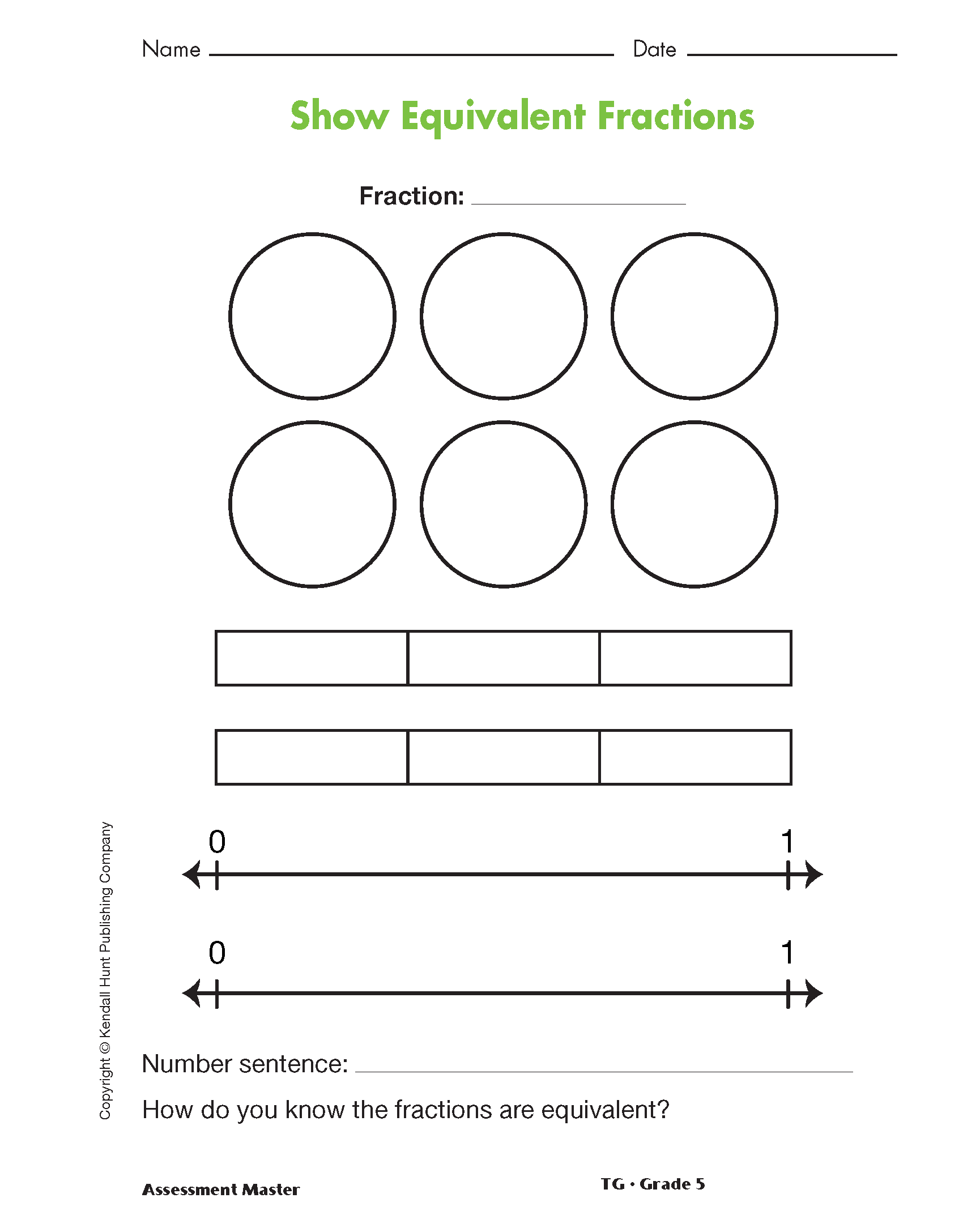
Display the Show Equivalent Fractions Assessment Master. Ask students to take turns showing equivalent fractions:
- The first student chooses a fraction, writes the fraction as a number, and shows it using one of the representations: pictures of circles, pictures of rectangles, or a number line.
- The next student names a fraction equivalent to the first and uses the same model to explain why it is equivalent.
- A third student shows both fractions but uses a different representation. He or she writes a number sentence and then shows why they are equivalent.
Here is an example of how one round of this activity might proceed:
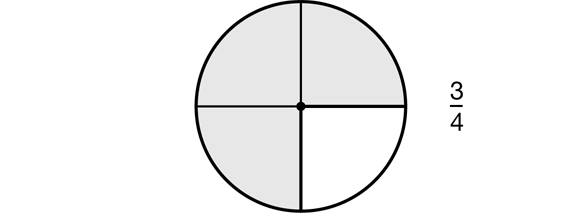
- In Step 1, a student might choose 3/4 and the circle model. Figure 7 shows what he or she would show on the display.
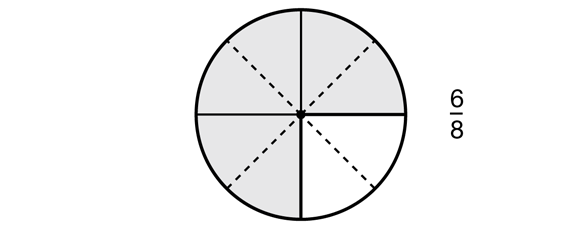
- In Step 2, a different student chooses a fraction that is equivalent to 3/4 , for example 6/8. He or she uses the same representation to show this fraction, in this case the circle model. Figure 8 demonstrates what is shown on the display. The student explains that 3/4 is equivalent of 6/8 because the size of the shaded regions is the same.
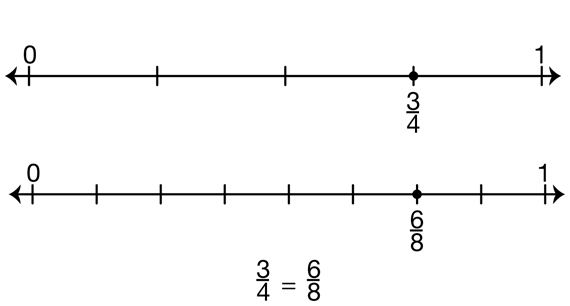
- In Step 3, a third student uses a different model to show that 3/4 and 6/8 are equivalent, this time using number lines. Figure 9 shows what is on the display. The student writes 3/4 = 6/8 and explains that 3/4 and 6/8 are the same distance from 0.
Continue the activity until several fractions and equivalent fractions have been discussed.
As students present their fractions on the display, ask:
Distribute copies of the Show Equivalent Fractions Assessment Master. Instruct students to do the following, just as they did in the Summarizing the Lesson activity, but independently:
- Choose a fraction and write it as a number.
- Show the fraction using one of the representations (e.g., number line).
- Show an equivalent fraction using the same model (e.g., number line).
- Show both fractions using a different representation (e.g., rectangles).
- Write a number sentence.
- Explain how they know the fractions are equivalent.