Modeling Division
Est. Class Sessions: 2–3Developing the Lesson
Part 2. The Column Method
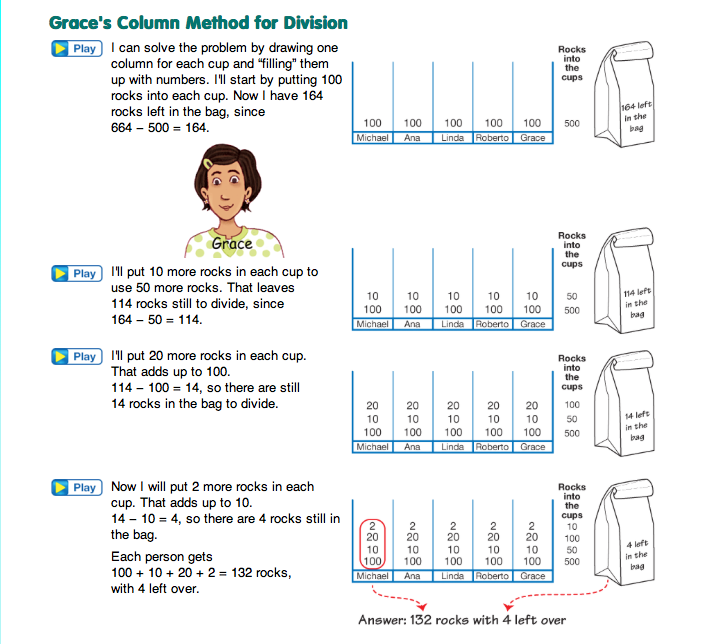
Model Division. Read the opening problem of the Modeling Division pages in the Student Guide as a class. Have partners discuss the problem about Grace's rocks using Questions 1–4. At this point, it is important that they not use a paper-and-pencil algorithm, such as long division or the partial quotients method, or a calculator to solve the problem. Encourage students to use words, drawings, and numbers to show their solutions. Be sure to allow enough time for students to work on their own methods before reading through Grace's method on the following page or suggesting computational strategies. This will provide a sense of how students approach division problems as well as their understanding of the underlying concepts.
After students solve the problem and check to see if their answers are reasonable as described in Question 4, ask two or three students to share their solutions with the class.
Introduce Grace's Column Method. Ask students to read through Grace's solution and then explain it to a partner. In her solution, Grace demonstrates the column method for dividing by a one-digit divisor. Explore the column method with the class using Questions 5–9 as a guide for the discussion. Be sure to discuss the meaning of the remainder and the conventions for showing the remainder in a solution to a problem. See Content Note.
Question 10 asks students to draw their own column model to solve 837 ÷ 5.
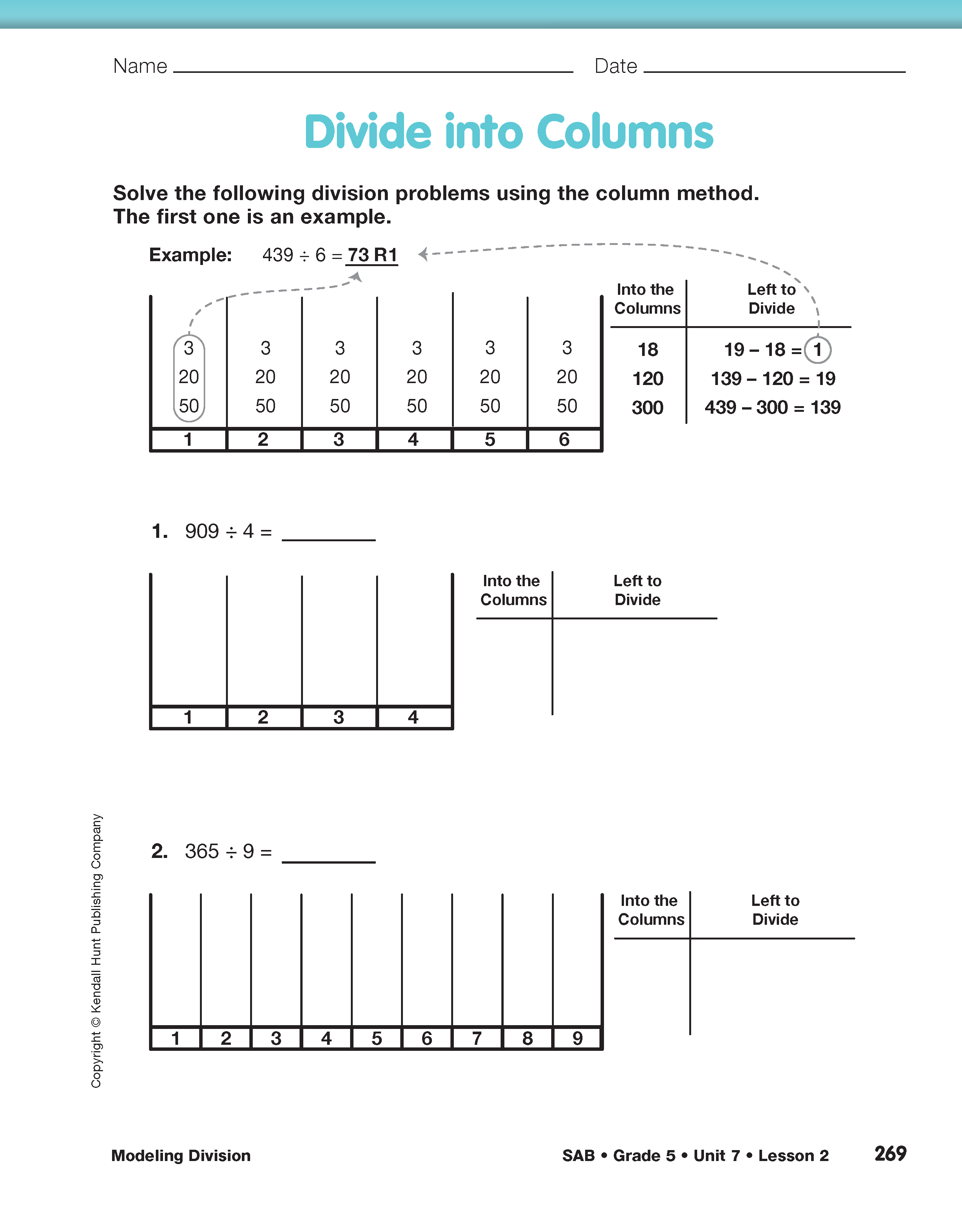
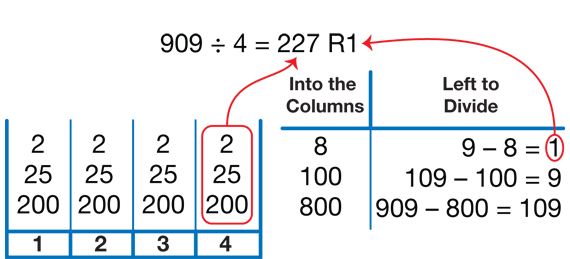
Practice the Column Method. Have students complete the Divide into Columns pages in the Student Activity Book. First, have students explain the example to a partner. As students work on the problems, ask questions to help students make connections between the representation and the division problems. See Figure 2.
Ask: