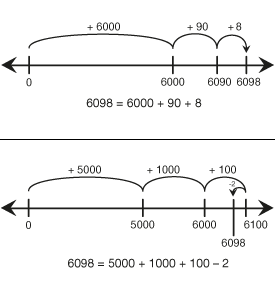
Students develop flexibility composing and decomposing large numbers based on place value concepts. They use moves on number lines to represent moves of ones, tens, hundreds, and thousands to develop mental math skills.
Content in this Lesson
- Showing partitions of numbers using number lines and number sentences (e.g., 1705 = 1000 + 700 + 5) [E1].
- Recognizing that different partitions of the same number are equal (e.g., 200 + 30 + 7 = 200 + 20 + 17) [E1].
- Representing addition and subtraction problems using number lines [E2, E3].
Daily Practice and Problems E–H
Assessment in this Lesson
| Assessment | Expectation Assessed |
|---|---|
|
Big Base-Ten Hoppers Check-In: Questions 13–19 Student Guide Page 122 |
|