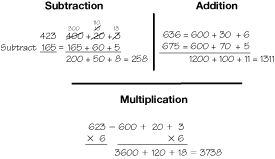
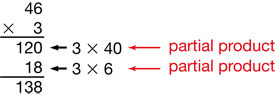
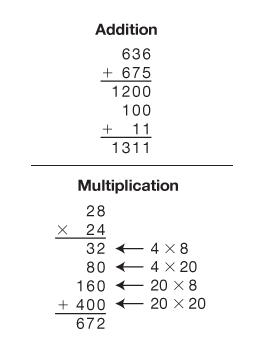Two commonly used methods for recording work while solving multiplication problems are presented: the all-partials method and the compact method (the United States' traditional multiplication algorithm). Both involve breaking numbers into their base-ten parts and multiplying the parts. The problems in the lesson involve 1-digit by 2-digit multiplication.
Content in this Lesson
- Multiplying 2-digit numbers by 1-digit numbers using paper-and-pencil methods (all-partials and compact) [E8].
- Choosing appropriately from among mental math and paper-and-pencil methods to multiply whole numbers [E10].
Daily Practice and Problems EE–HH
Assessment in this Lesson
| Assessment | Expectation Assessed |
|---|---|
|
Paper-and-Pencil Multiplication Questions 9–11 Student Guide Page 160 |
|
|
DPP Item GG Multiplication Quiz: 9s Teacher Guide - digital |
|
|
DPP Item HH Finding n Teacher Guide - digital |
|