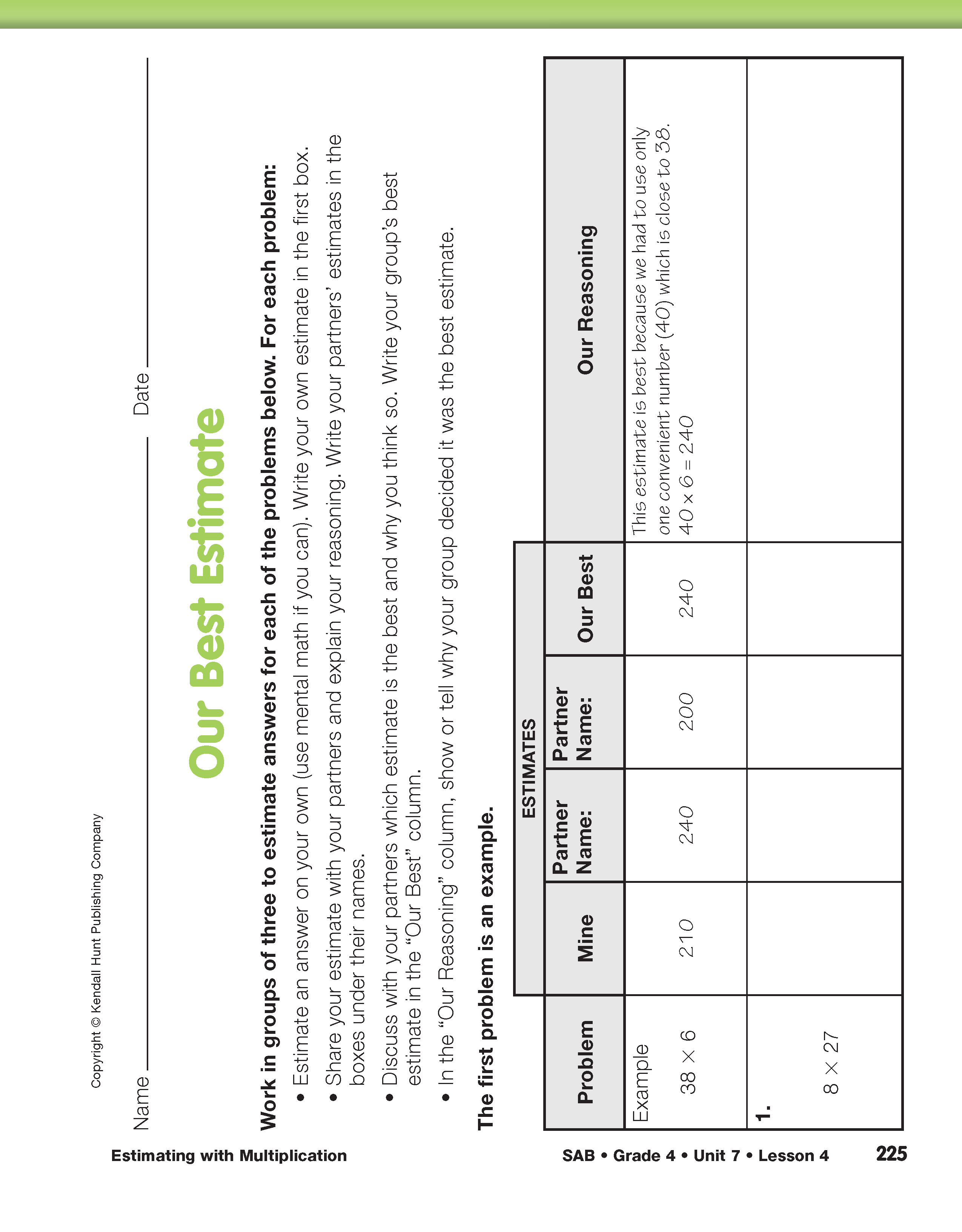
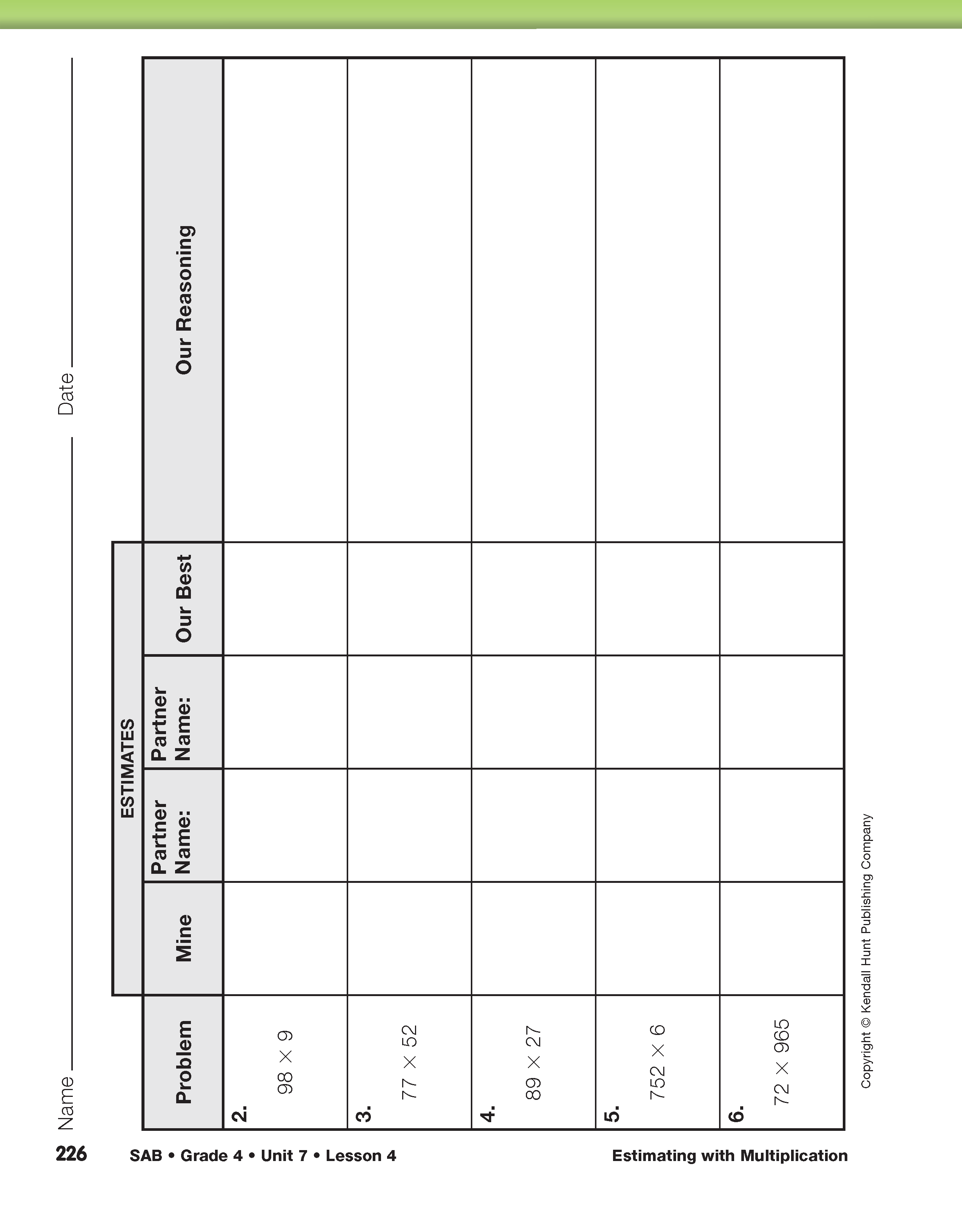
Estimating with Multiplication
Est. Class Sessions: 2Summarizing the Lesson
Use the Our Best Estimate pages in the Student Activity Book to summarize the lesson. Emphasize the quick and efficient use of mental math as students estimate answers to the multiplication problems. In this activity, students communicate their reasoning to their partners about why they chose a particular estimation strategy or convenient number. While problems involving estimation do not necessarily have a “right” answer, it is important that students justify their strategies to each other and reach consensus about which of their estimates is “best.” Encourage students to choose their estimates without comparing to exact answers found with a calculator. Students should also be able to choose, explain, and justify strategies based on how easy they are to do mentally, how efficient they are, and how accurate they are.
After students have completed a few of the problems in their small groups, have one or two groups explain their best estimates for a few of the problems to the whole class, and then compare their estimates to those reached by other groups. Again, it is important to emphasize that two estimates can be different and still both be good estimates. The key is that students are able to explain why they estimated the way they did and that the estimates are reasonably close to an exact answer.
Assign the Operations, Divisibility, and Estimation Quiz Assessment Master.